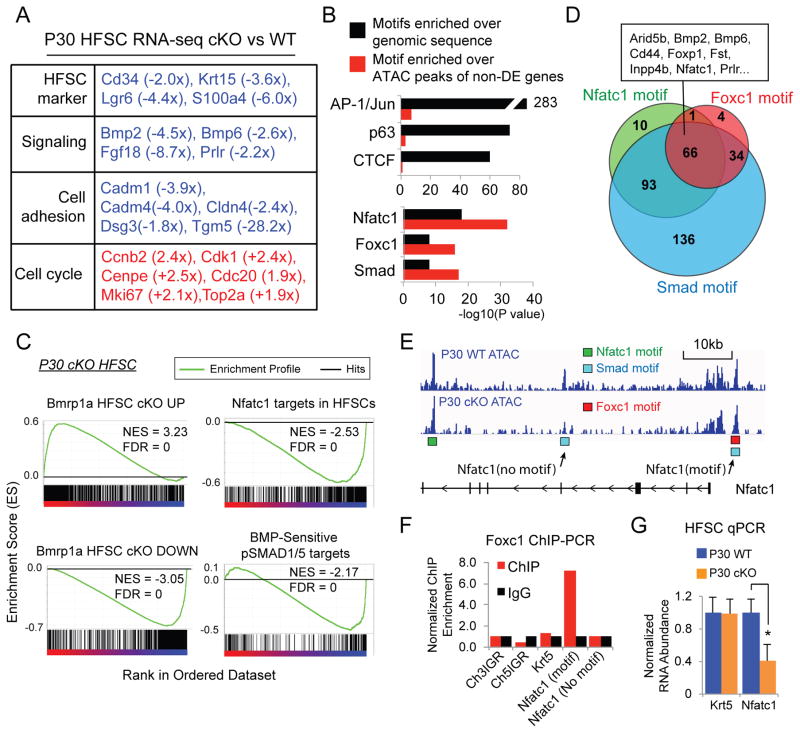
Fig. 4. Foxc1 activates quiescence gene networks.
(A) Functional classification of selected differentially expressed gene in P30 KO HFSCs. (B) Comparison of enriched TF motifs against genomic sequences and against the peaks covering the non-differentially expressed (non-DE) genes in P30 KO HFSCs. (C) GSEA of BMP responsive genes and Nfatc1 targets in P30 KO HFSCs. (D) Venn diagram of the differentially expressed genes in P30 KO HFSCs that contain motifs of Foxc1, Smad and Nfatc1 shows a co-regulated gene network. (E) ATAC-seq track of the Nfatc1 locus. Location of Nfatc1, Smad and Foxc1 motifs are shown in the peak region. (F) ChIP-PCR analysis of Foxc1 confirms association of Foxc1 to the predicted binding site in the Nfatc1 locus. (G) Differential expression of Foxc1 targets, Nfatc1, in the WT and KO HFSCs (* p<0.05).