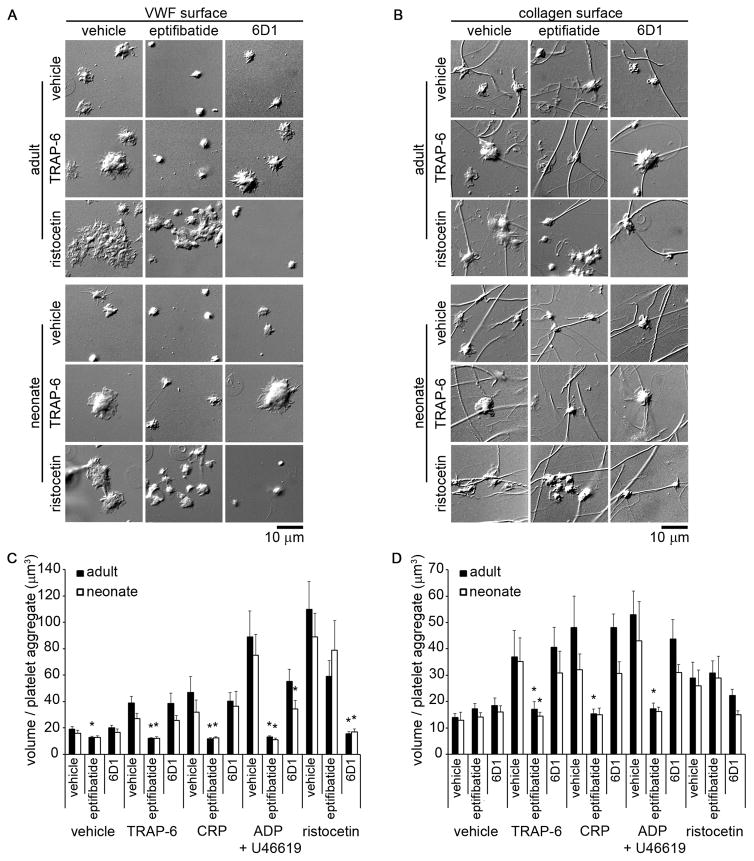
Figure 4. Effect of glycoprotein (GP) IIbIIIa and GPIb inhibition on adult and neonatal platelet adhesion and aggregation under static conditions.
Representative differential interference contrast images of adult and neonatal platelet aggregates formed on coverslips coated with 100 μg/mL von Willebrand factor (VWF) (A) or 100 μg/mL fibrillar collagen (B). Adult and neonatal citrated whole blood were incubated with a glycoprotein (GP) IIbIIIa inhibitor (eptifibatide; 20 μg/mL), a GPIb function blocking antibody (6D1; 20 μg/mL), or vehicle for 10 min at 25°C and then treated with thrombin receptor activator peptide-6 (TRAP-6; 10 μM), collagen related peptide (CRP; 10 μg/mL), adenosine 5′-diphosphate (ADP) + U46619 (10 μM), ristocetin (1 mg/mL), or vehicle for 10 min. Mean volume of adult and neonatal platelet aggregates positive for CD62P-FITC formed on coverslips coated with VWF (C) or fibrillar collagen (D). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; Nadult = 3 and Nneonate = 3; *P < 0.05 with respect to vehicle treated samples.