Fig. 1.
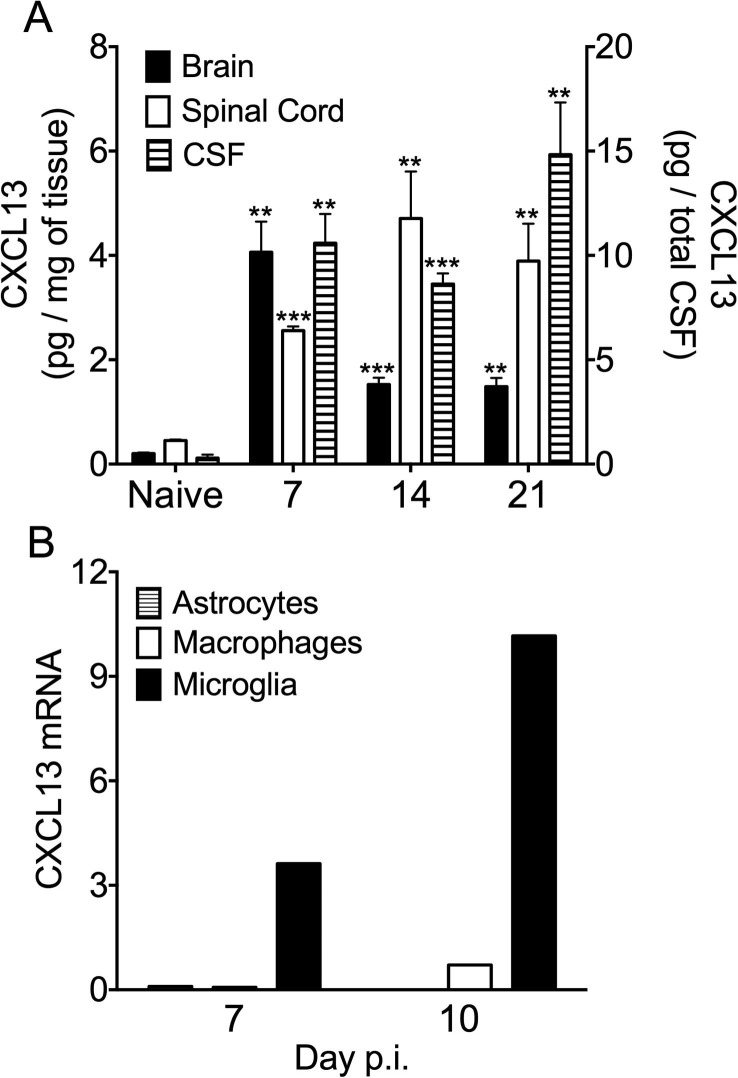
Microglia are a primary source of CXCL13. (A) Brain, spinal cord and CSF CXCL13 levels from individual mice were assessed by ELISA. Brain and spinal cord data are expressed as the mean CXCL13 per mg of tissue ±SEM (left-hand y axis) of 6–8 mice per time point from two independent experiments. Typical weights for brain and spinal cord were 397 ± 10 mg and 80 ± 2 mg, respectively. CSF data are expressed as the mean CXCL13 per total CSF volume ± SEM (right-hand y axis) of 3–4 mice per time point from one experiment. Total volume of mouse CSF is estimated to be 40 μl (Johanson et al., 2008). Significant differences between naïve and infected samples determined by the unpaired t test are denoted by **(p < 0.01) and ***(p < 0.005). (B) Relative transcript levels of CXCL13 in FACS-purified GFP+CD45- astrocytes (striped bars), CD45hiCD11b+F4/80+ monocyte-derived macrophages (empty bar) or CD45lo microglia (solid bar) derived from pooled spinal cords of 6–8 GFAP-GFP mice per time point collected at 7 and 10 days p.i. were assessed by real-time PCR. Transcript levels are relative to GAPDH.