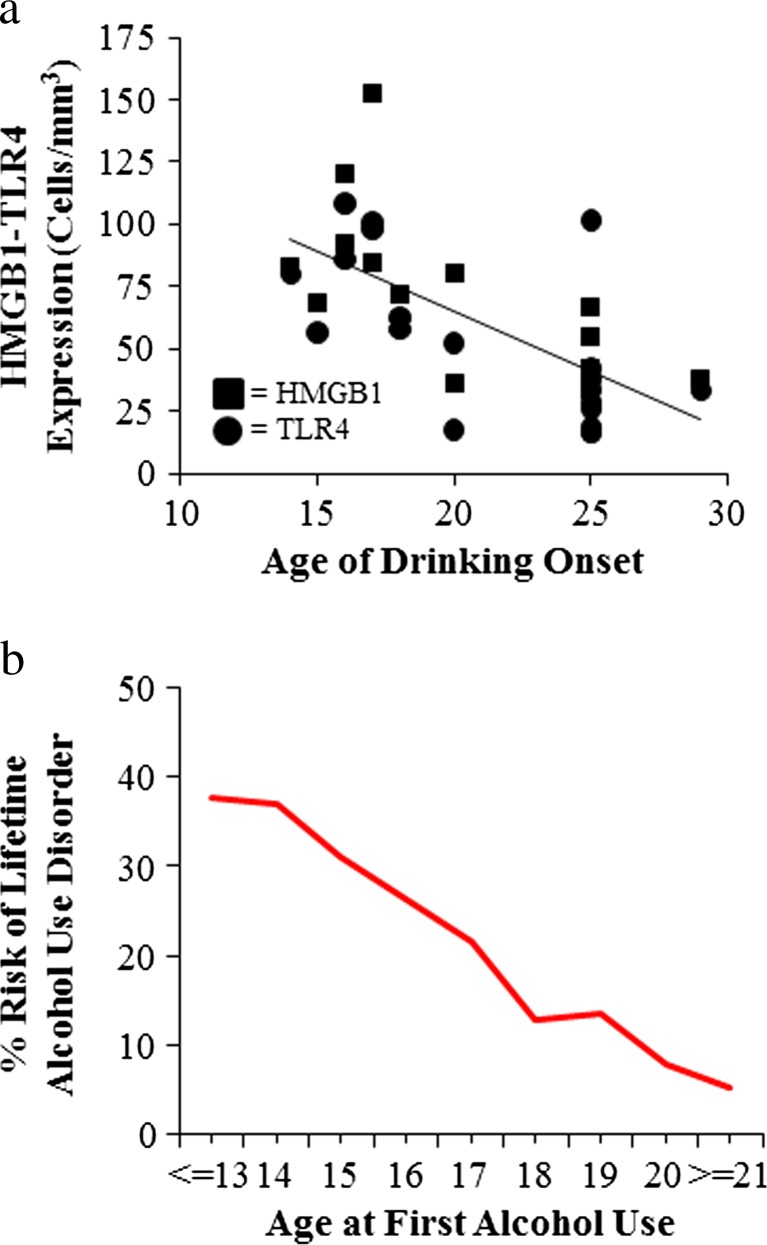
Fig. 7.
Risk of alcoholism and induction of innate immune genes correlate with age of drinking onset in humans. a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) expression in the post-mortem human brain is negatively correlated with age of drinking onset adapted from Vetreno et al. (2013). b An earlier age of drinking onset is predictive of an increased likelihood of developing an alcohol use disorder during an individual’s lifetime. Adapted from Grant (1998)