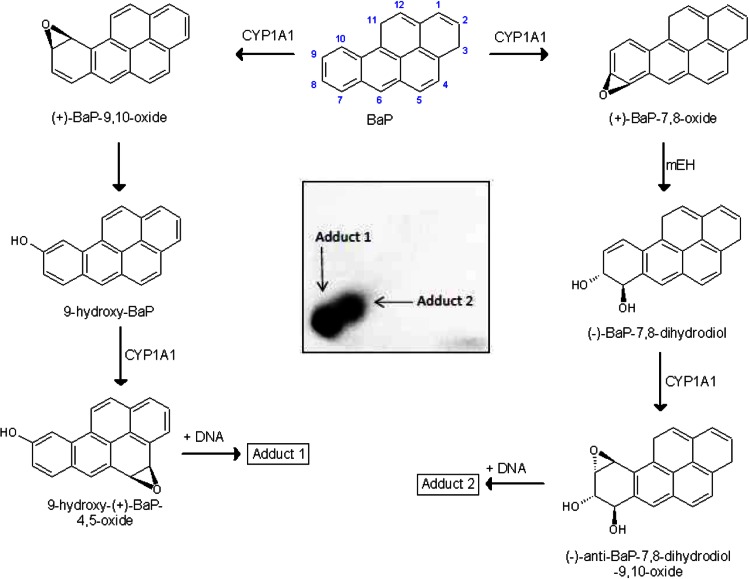
Fig. 1.
Proposed pathways of biotransformation and DNA adduct formation of BaP catalyzed by CYP1A1 and mEH. As shown in the left part of the figure, the two-step activation process by CYP1A1 leads to the formation of 9-hydroxy-BaP-4,5-oxide that can react with deoxyguanosine in DNA (adduct 1). As shown in the right part of the figure, the typical three-step activation process by CYP1A1 followed by hydrolysis by mEH leads to BPDE which forms dG-N 2-BPDE (adduct 2) (adopted from [15]). Inset autoradiographic profile of BaP-DNA adducts formed by hepatic microsomes of rats pretreated with BaP as evaluated by thin-layer chromatography 32P-postlabeling as described previously [15]; the arrows show adducts 1 and 2