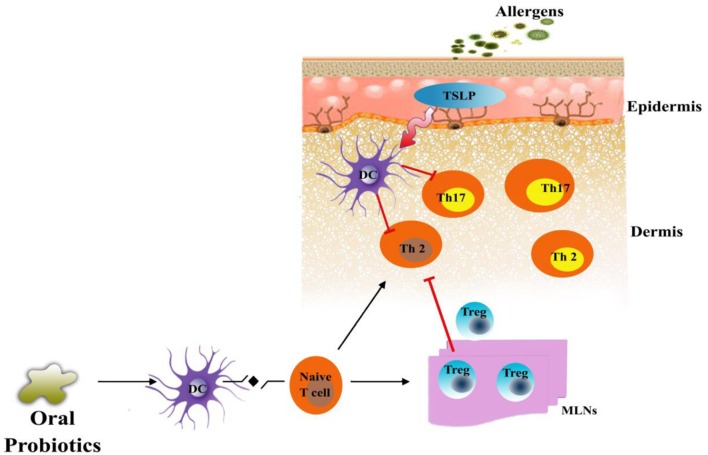
FIGURE 1.
Proposed mechanism of probiotics in an animal model of AD. Exposure of atopic skin to a potential allergen enhances the expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) that is known to activate dendritic cells (DC). Stimulated dendritic cell direct differentiation of naïve T-cell into Th2 cells and Th17 cells which, are known as the mediators of allergic inflammation in skin. Probiotics could inhibit the allergic inflammation by increasing the population of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the mesenteric lymph nodes of patients. These Tregs could migrate to the site of inflammation and suppress the Th2 and Th17 mediated allergic response or directly reduce the expression of TSLP.