Figure 1. The cold water extract of Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) inhibits viral replication and plaque formation in a broad range of influenza strains in vitro.
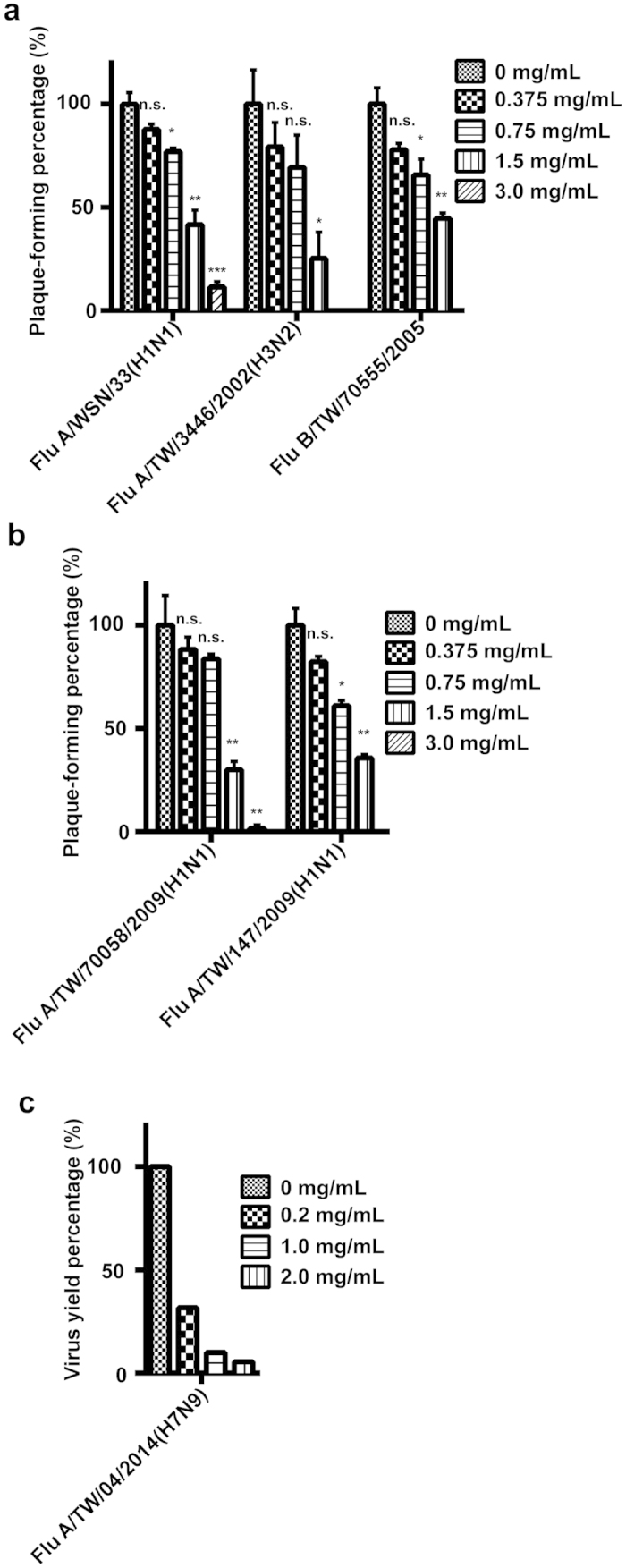
(a) The influenza virus strains A/WSN/33(H1N1), A/TW/3446/02(H3N2), and B/TW/70555/05, and (b) the oseltamivir-resistant strains A/TW/70058/09(H1N1) and A/TW/147/09(H1N1), propagated on MDCK cells, all exhibited dose-dependent reductions in virus plaque formation after treatment with 0.375, 0.75, 1.5, and 3.0 mg/ml of Spirulina extract. Data represent the mean ± SD for three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test, and used as the basis to label results as ns, not significant; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; or ***P ≤ 0.001. (c) The TCID50 assay showed that Spirulina extract reduced virus production of the influenza A/TW/04/2014 (H7N9) virus.
