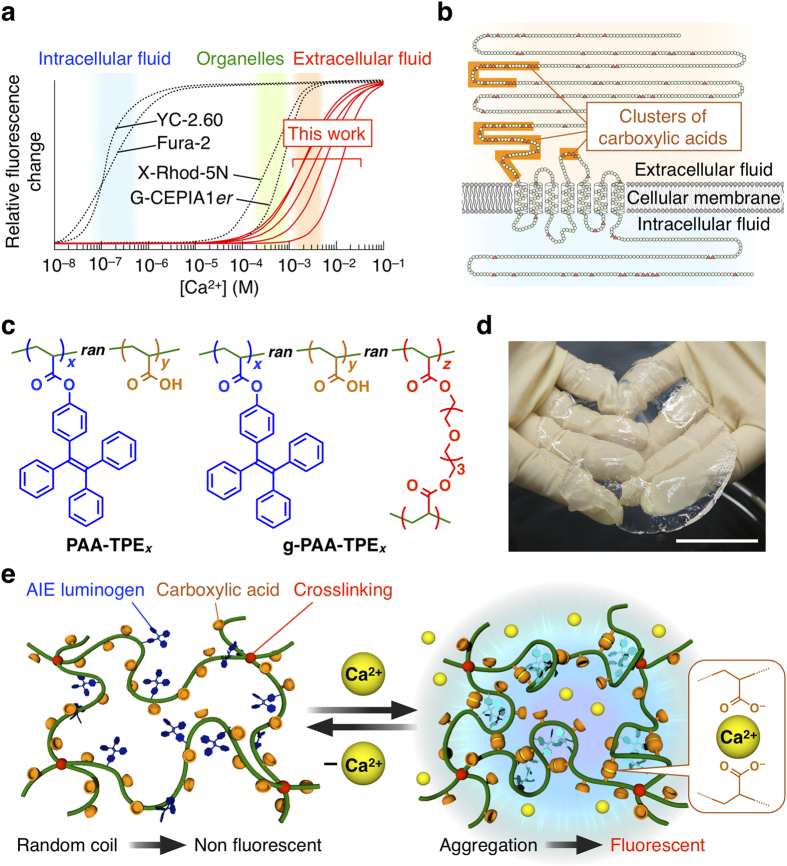
Figure 1. Design of Ca2+ sensors based on tetraphenylethene (TPE)-appended polyacrylic acid (PAA).
(a) Schematic illustration showing the relationship between Ca2+ concentrations in biological systems and applicable concentration ranges of typical Ca2+ indicators (Fura-224, X-Rhod-5N25, YC-2.6029 and G-CEPIA1er31). (b) Schematic illustration of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaSR)4. (c) Chemical structures of PAA-TPEx and g-PAA-TPEx, where x, y and z indicate the molar ratios (contents) of TPE, PAA and crosslinker, respectively (see also Table 1), and ran means that the monomer sequence is random, i.e., random copolymer. (d) Photograph of a sheet of swollen g-PAA-TPE0.02. Scale bar, 5 cm. (e) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of Ca2+ sensing with g-PAA-TPEx.