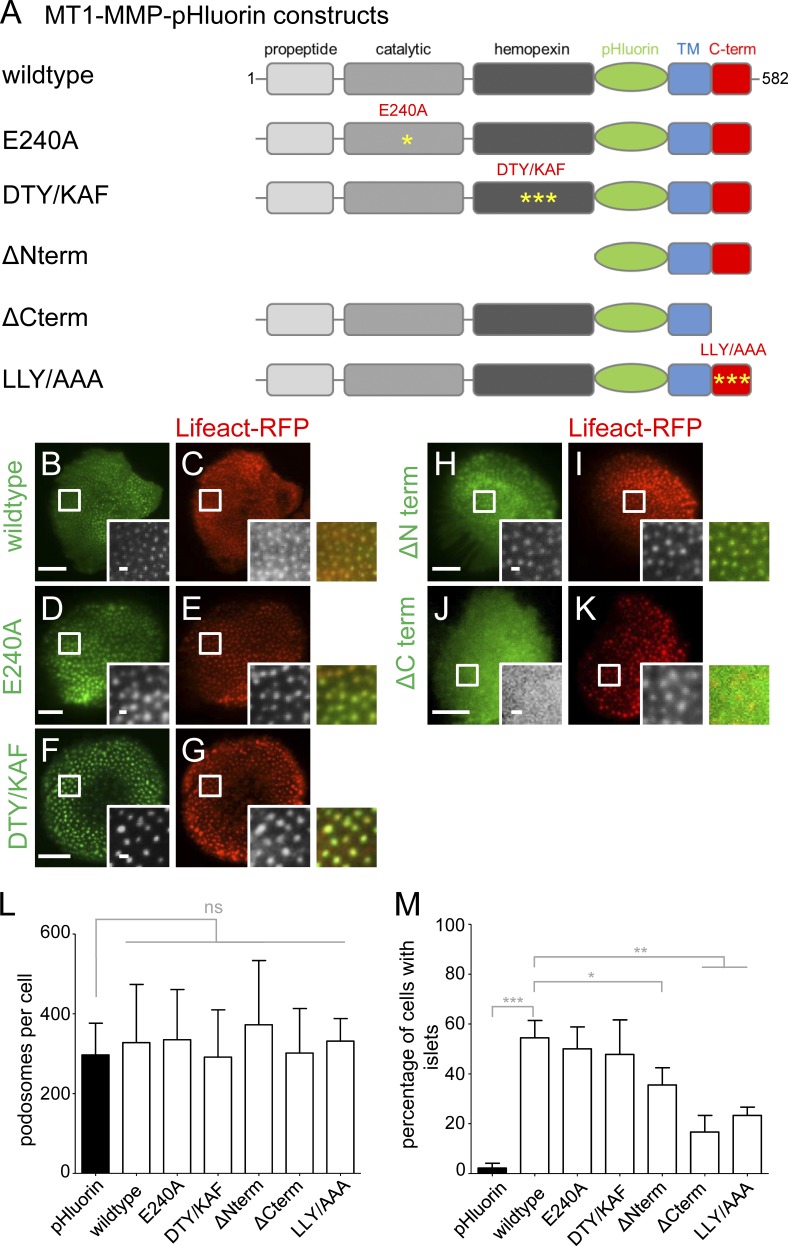
Figure 8.
The cytoplasmic tail of MT1-MMP is necessary for localization of the protease to podosomes. (A) Domain structure of MT1-MMP, containing a propeptide domain absent in the activated protease, a catalytic domain harboring protease activity, a hemopexin domain involved in oligomerization, a transmembrane domain, and a C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. pHluorin was inserted as an intramolecular tag N terminally of the transmembrane domain and is thus extracellular on the surface-exposed protease. First and last amino acid residues are indicated. Yellow asterisks indicate respective point mutants (E240A; DTY/KAF, D385K, T412A, Y436F; LLY/AAA, L571A, L572A, L573A). (B–K) TIRF micrographs of macrophages expressing indicated MT1-MMP-pHluorin constructs (green), together with Lifeact-RFP (red). White boxes indicate areas of detail images shown in black and white insets, with colored merges on the right. Note absence of ΔCterm construct from podosomes (J and K). Bars: 10 µm; (insets) 1 µm. (L and M) Statistical evaluation of podosome numbers in cells expressing indicated MT1-MMP-pHluorin constructs (L) or of MT1-MMP-pHluorin siRNA-insensitive constructs localizing to islets in cells depleted for endogenous MT1-MMP (M). For each value, 3 × 5 cells from three different donors were evaluated. Bars represent mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001. For specific values, see Table S2.