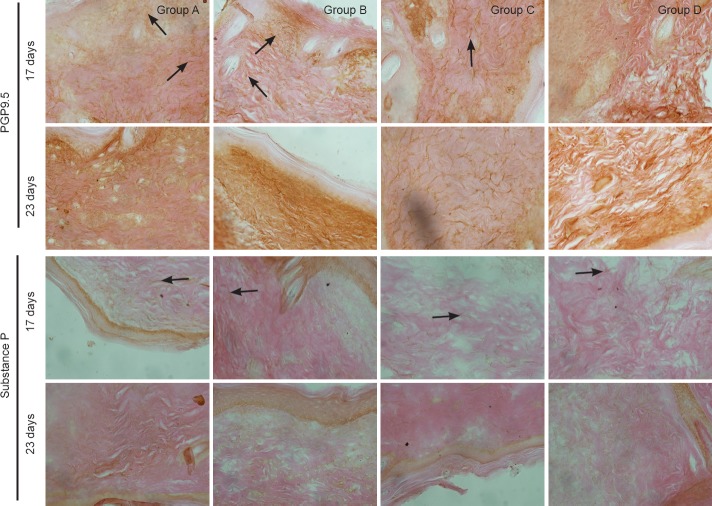
Figure 5.
Effect of substance P combined with epidermal stem cells on PGP9.5 and substance P immunoreactivities in wounds of diabetic rats at 17 and 23 days after injury (immunohistochemical staining, × 400). In groups A and C at 17 days after injury, PGP9.5-immunoreactive fibers had regenerated and a large number of substance P-immunoreactive fibers were visible in healed wounds. In groups B and D, there were less regenerating fibers in healed wounds, and substance P-immunoreactive fibers were detected. In groups A and C at 23 days, PGP9.5-immunoreactive fibers were detected at the dermal and epidermal junction. Substance P-immunoreactive fibers had noticeably diminished. In groups B and D, the number of regenerating nerves had increased. Substance P-immunoreactive fibers were detected at the dermal and epidermal junction. Arrows show immunoreactivity. Group A: injection of substance P + human amniotic membrane in-cubated with epidermal stem cells around and at the center of the wound; group B: injection of 250 μL PBS + human amniotic membrane incubated with epidermal stem cells around and at the center of the wound; group C: injection of substance P + human amniotic membrane without epidermal stem cells around and at the center of the wound; group D: injection of 250 μL PBS + human amniotic membrane without epidermal stem cells around and at the center of the wound. PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; PGP9.5: protein gene product 9.5.