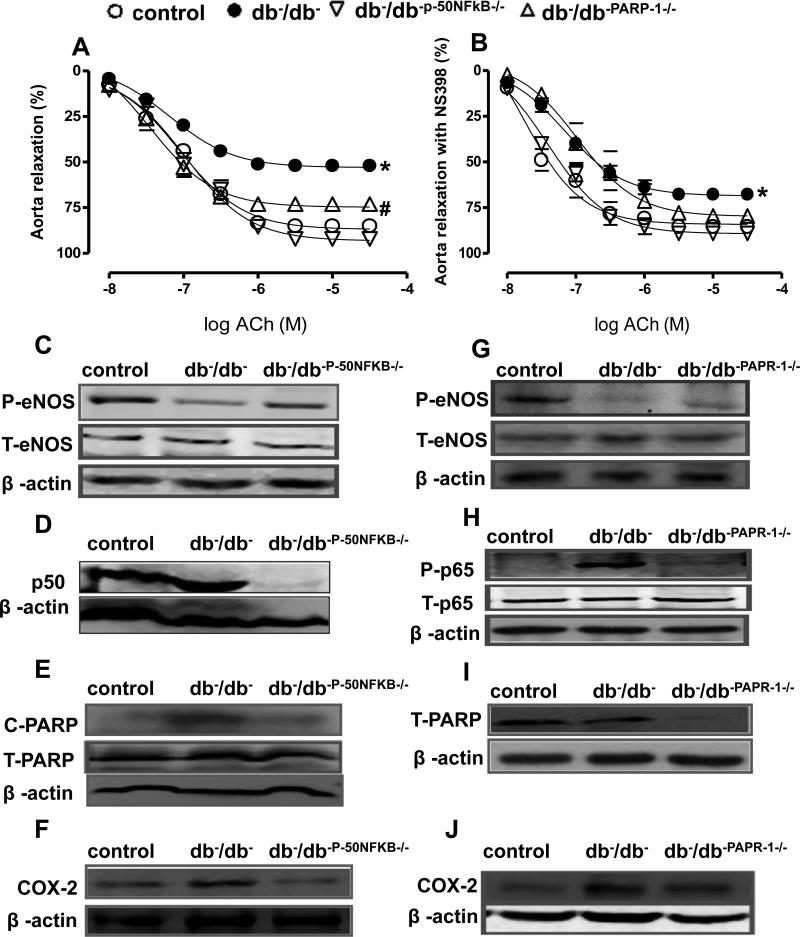
Figure 3. Effect of the NFκB inhibition on endothelium-dependent relaxation in thoracic aorta (n=10).
Endothelium-dependent relaxation in response to cumulative doses of ACh (10−8−3.10−5 M) in rings from aorta, pre-contracted with phenylephrine (PE, 10−5 M), from Control, db−/db−, db−/db-p- 50NFκB−/− and db−/db-PARP-1−/−, (A) and incubated with NS 398 (COX-2 inhibitor)(B) *P < 0.05 for db−/db− vs. control, db−/db-p-50NFκB−/− or db−/db-PARP-1−/− #P < 0.05 for db−/db-PARP-1 vs. control, db−/dbp-50NFκB−/−.
Western blot analysis and quantitative data (n=5) in homogenized thoracic aorta from control, db−/db−, and double knockout mice between db−/db− and p50NFκB (db−/db-p-50NFκB−/−) showing phosphorylated (P)-eNOS, total (T)-eNOS (C) p50NFκB (D), cleaved (c)-PARP-1 and total (T)-PARP-1 (E), COX-2 (F) and β-actin, and double knockout mice between db−/db− and PARP-1 male mice (db−/db-PARP-1−/−), showing phosphorylated (P)-eNOS, total (T)-eNOS (G) phosphorylated (P)-p-65 and total (T)-p-65 (H), total (T)-PARP-1 (I), COX-2 (J) and β-actin.