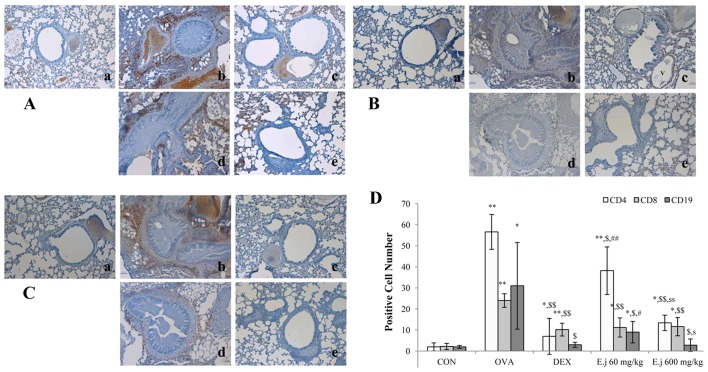
Figure 3.
Effects of E. japonicum on the numbers of Th, T and B cells in mouse lung tissue. (A) Representative images of CD4+ Th cells. (B) Representative images of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. (C) Representative images of CD19+ B cells. Immunopositive cells were counted in 5 randomly selected, non-overlapping fields (magnification, ×200) from 3 separately immunostained lung sections per animal. Treatment groups: panel a, control (CON); panel b, ovalbumin (OVA); panel c, dexamethasone (DEX); panel d, 60 mg/kg/day E. japonicum (E.j.); panel e, 600 mg/kg/day E. japonicum. (D) Quantitative analysis of positively-stained cells. *p<0.05 vs. CON; **p<0.001 vs. CON; $p<0.05 vs. OVA; $$p<0.001 vs. OVA; #p<0.05 vs. DEX; ##p<0.001 vs. DEX; sp<0.05 vs. 60 mg/kg/day E.j; ssp<0.001 vs. 60 mg/kg/day E.j.