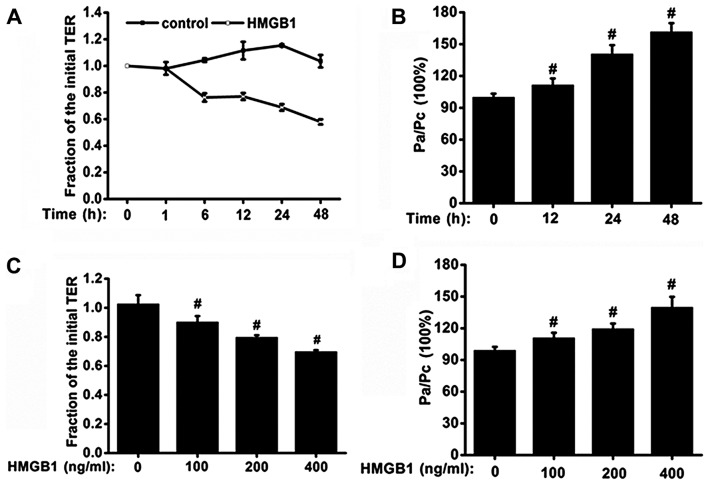
Figure 1.
Time- and concentration-dependent effects of high-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) on airway epithelial barrier function. 16HBE cells were seeded in 12-well Transwell inserts, grown for 3–5 days, and serum-deprived overnight. (A and B) To investigate the time-dependent effects, epithelial cell monolayers were treated with 400 ng/ml HMGB1 or medium only (n=6 experiments). (C and D) To examine the concentration-dependent effect, the epithelial cell monolayers were treated with 100, 200 and 400 ng/ml HMGB1, or medium for 24 h (n=6 experiments). (A and C) Transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) was measured with ERS-2, and the levels of TER were normalized to those prior to stimulation with HMGB1 or medium only (control); (B and D) the rates of FITC-dextran permeability were normalized to the ratio between HMGB1 and the medium only (control) stimulation, which was denoted by Pa/Pc. P-values were calculated using the ANOVA test. #P<0.05 vs. control.