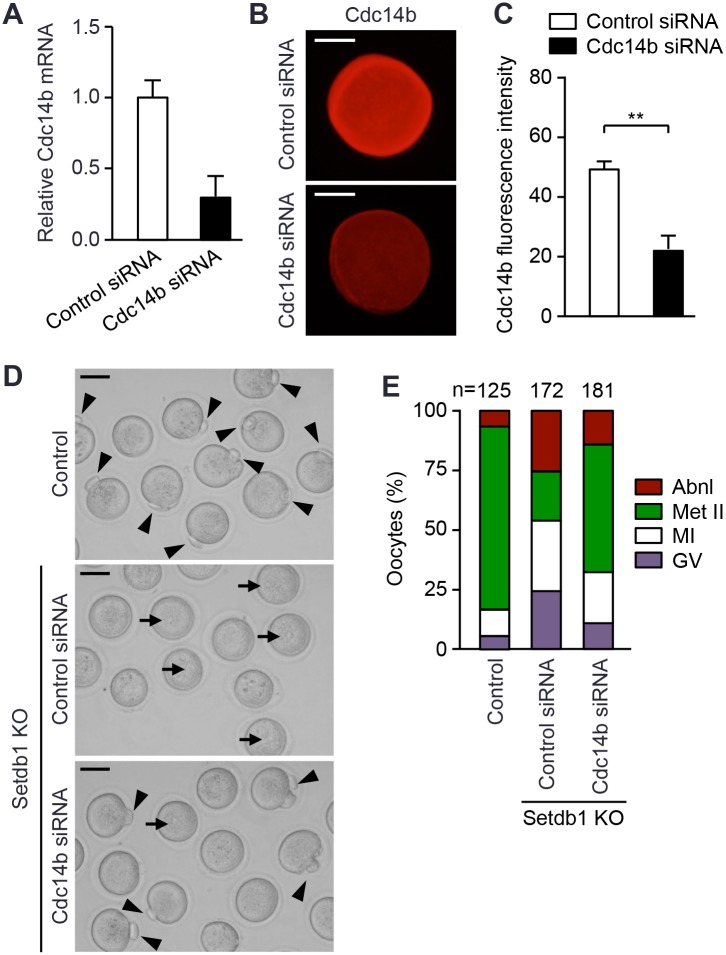
Fig 5. Cdc14b depletion in Setdb1 KO oocytes alleviates meiotic arrest.
GV oocytes were harvested from control and Setdb1 KO mice. Setdb1 KO oocytes were microinjected with either control siRNA or Cdc14b siRNA. These oocytes, as well as control GV oocytes, were incubated in IBMX-containing medium for 24 hours to allow siRNA-mediated Cdc14b depletion to occur, followed by in vitro maturation in IBMX-free medium for 20 hours. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of Cdc14b mRNA 24 hours after microinjection. Shown are relative Cdc14b mRNA levels in oocytes injected with control siRNA and Cc14b siRNA (mean ± SEM of duplicate assays). (B, C) IF analysis of Cdc14b 24 hours after microinjection. (B) Representative IF images of oocytes injected with control siRNA or Cdc14b siRNA. Scale bars, 35 μm. (C) Quantification of fluorescence intensity of Cdc14b. Twenty oocytes injected with control siRNA and 20 oocytes injected with Cdc14b siRNA were analyzed, and the data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were made using unpaired t-test. **P < 0.01. (D, E) Determination of meiotic stages after 20 hours of in vitro maturation. (D) Representative bright-field microscope images of control oocytes and Setdb1 KO oocytes injected with control siRNA or Cdc14b siRNA. Arrowheads and arrows indicate the polar bodies (characteristic of Met II oocytes) and the prominent nucleoli (characteristic of GV oocytes), respectively. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) Percentages of oocytes at different meiotic stages (GV arrested, MI, Met II, and abnormal). In total, 200 KO oocytes were injected with control siRNA and another 200 with Cdc14b siRNA, and 172 and 181 of them, respectively, survived.