Figure 7.
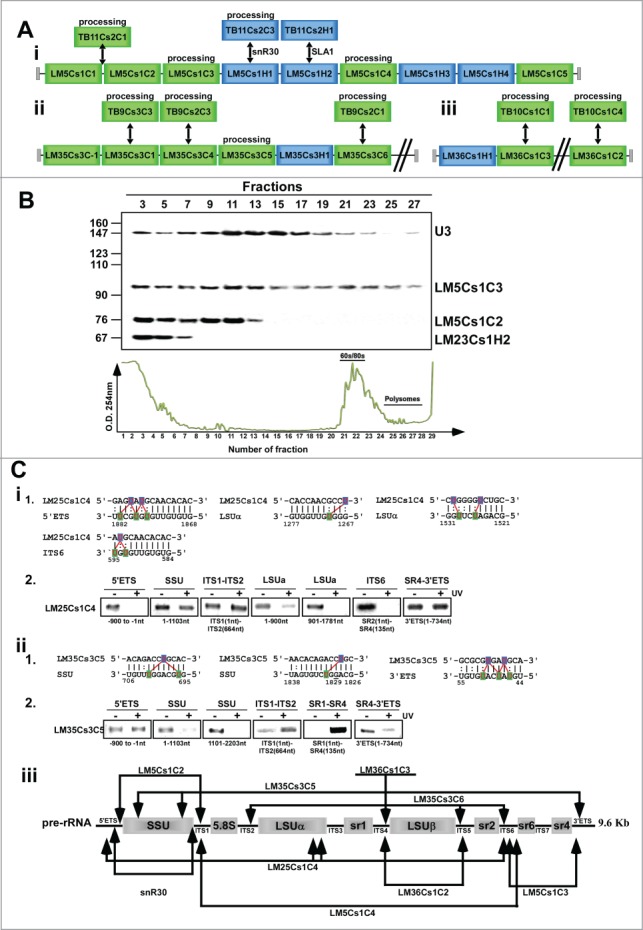
L. major snoRNAs implicated in rRNA processing. (A) L. major homologues to T. brucei snoRNAs implicated in rRNA processing. (B) Genomic relatedness between clusters encoding snoRNAs involved in rRNA processing. i. LM5Cs1 and TB11Cs2; ii. LM35Cs3/TB9Cs3; iii. LM36Cs1/TB10Cs1. B - Migration of the snoRNAs on sucrose gradients. RNPs were prepared and fractionated as described in Materials and Methods. RNA was extracted from the fractions and separated on 10% polyacrylamide-denaturing gel, and subjected to Northern analysis with the indicated probes. The sizes of pBR322 DNA-MspI digest marker are indicated on the left, and the identity of the RNAs on the right. (C) “RNA walk” analysis to validate snoRNA-rRNA interactions. i-1- The proposed cleavage sites of LM35csC5 and LM25Cs1C4 and proposed interaction domain of LM25Cs1C4 and pre-rRNA with rRNA. i-2- “RNA walk” analyses of the interaction site of the 2 snoRNAs. RT-PCR of rRNA domains interacting with TB25Cs1C4. cDNA was prepared from RNA affinity selected with LM25Cs1C4 from total RNA prepared after AMT cross-linking. The domains and the size of the amplified fragments are indicated. ii (1 and 2). The same as in (i) but for LM35CSC5. iii. Schematic representation of the interaction site and potential cleavages by snoRNA implicated in rRNA processing. The proposed cleavage site of pre-rRNA is indicated by arrows.
