Figure 3.
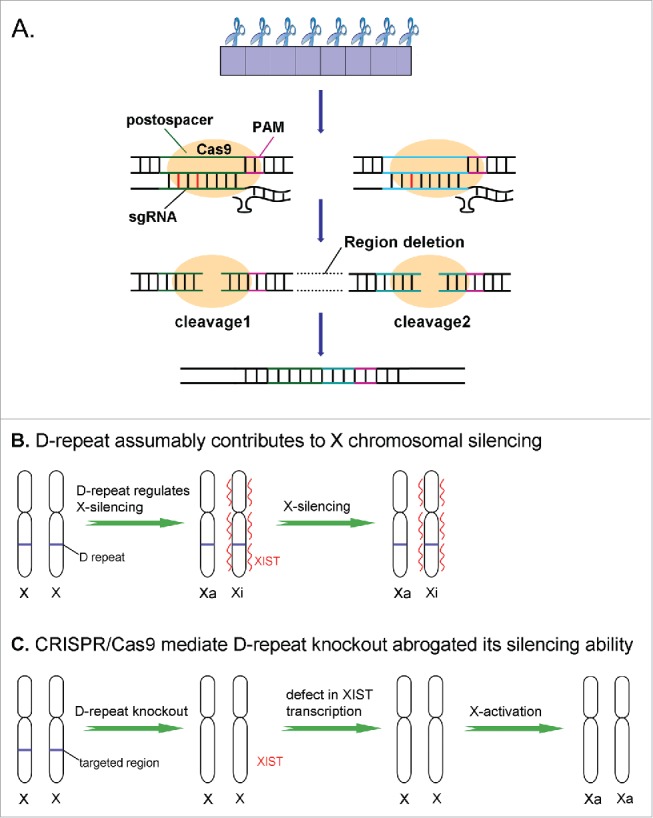
Summary of the CRISPR/Cas9 mediated D-repeat knockout and its roles on X-inactivation (A) Schematic representation of D-repeat knockout in XIST using CRISPR/Cas9 system. The Cas9 protein binds to the sgRNA scaffold and in the presence of the postorspacer sequence and the PAM sequence it generates a cleavage. The cleavage triggers the endogenous cellular DNA repair machinery that catalyzes non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). The red segment indicated the misparing between sgRNA and genome site. The green part represents the OTS1, the blue represents the OTS2. (B) D-repeat regulated the expression of XIST (red) on the inactive X chromosome (Xi). Subsequently, the XIST RNA coats the whole X chromosome induced the X-inactivation.(C) CRISPR/Cas9 mediated D-repeat knockout resulted in the downregulated expression of XIST, which lead to the compromise of X-inactivation.
