Figure 1.
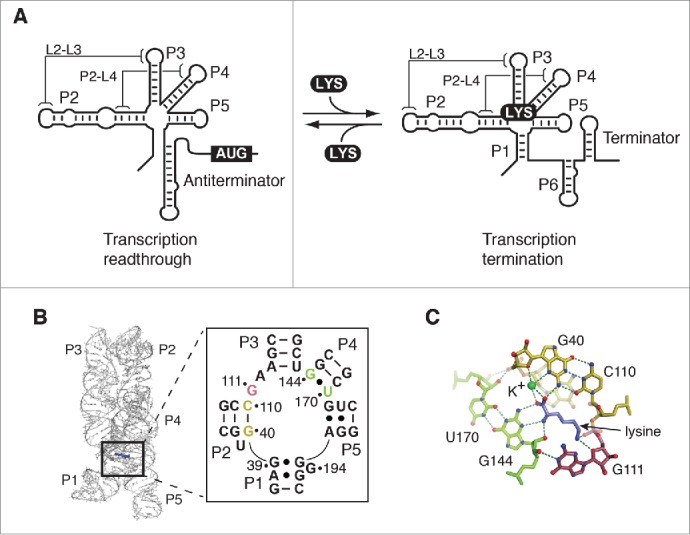
Structure and function of the lysine riboswitch. (A) Schematic representation of the lysine riboswitch regulation mechanism. In absence of lysine, the lysine lysC riboswitch adopts a conformation in which transcription readthrough is allowed. In this configuration, the P1 stem is presumably not formed in the aptamer domain. However, upon lysine (LYS) binding, the P1 stem is stabilized, which in turn allow the formation of a transcription terminator. Tertiary interactions involving L2-L3 and P2-L4 are shown. (B) Structure of the lysine riboswitch aptamer domain. The crystal structure of the lysine aptamer bound to lysine is shown.16,17 Lysine is represented in violet and selected nucleotides involved in the lysine-binding site are shown. The insert shows base pair G40-C110 and the wobble pair G144•U170 in yellow and green, respectively. G111 is represented in magenta. The nucleotide nomenclature is based on previous studies.26,27 (C) Representation of the lysine-binding site. The base pair G40-C110 and the wobble pair G144•U170 are shown in yellow and green, respectively, and G111 is represented in magenta. While pairs G40-C110 and G144•U170 interact with the carboxyl end of lysine, G111 is involved in the recognition of the ε-ammonium group. Lysine is shown in violet. A potassium ion (K+) coordinating lysine is shown in green. Hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dotted lines. Nitrogen and oxygen atoms are shown in blue and red, respectively.
