Figure 5.
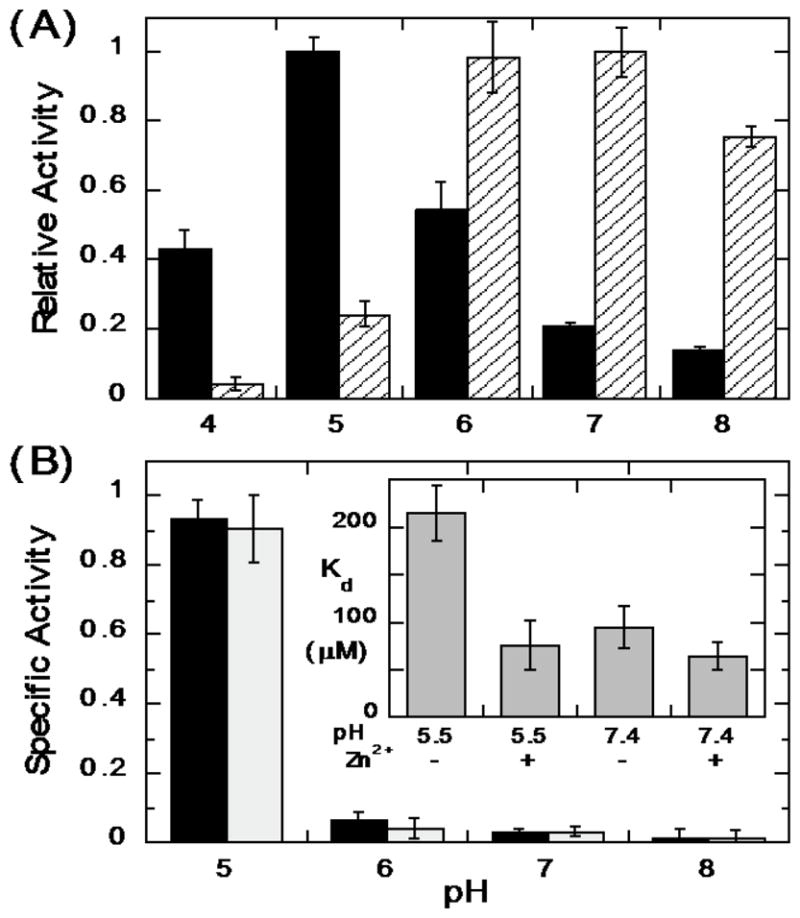
The pH dependence of LmPLC activity towards POPC presented in micelles and vesicles. (A) Enzyme activities relative to the enzyme maximal activity towards POPC (6 mM) dispersed in 20 mM Triton X-100 for LmPLC (black) and BcPLC (hatched). (B) Specific activity (μmol min−1 mg−1) of LmPLC towards 4 mM POPC (black bar) or POPC /cholesterol (4 mM /2 mM) (grey bar) SUVs as a function of pH. The inset in (B) shows the apparent dissociation constant (Kd) of LmPLC (10 nM) binding to POPC/POPG (0.95/0.05) SUVs at pH 5.5 (20 mM MES) or pH 7.4 (20 mM HEPES), with 150 mM NaCl, 50 μM Zn2+, and 1 mg/mL BSA. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n = 3 independent experiments.
