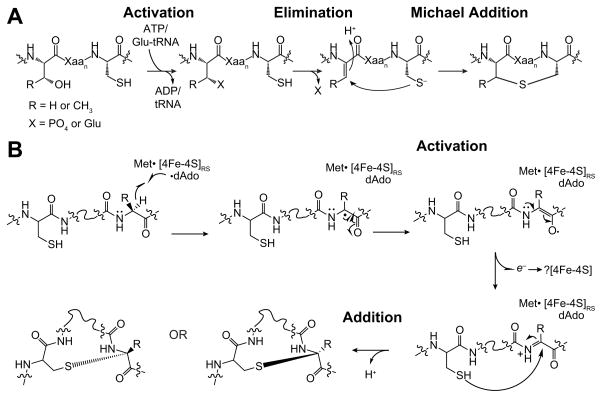
Figure 8.
Proposed mechanisms of thioether crosslink formation in lantipeptides and sactipeptides. (A) Mechanism of thioether crosslink formation in lanthipeptides. Substrate is activated to generate a reactive intermediate (Dha or Dhb), which undergoes Michael addition to generate the initial crosslink. (B) Proposed mechanism for radical-mediated thioether cross-links in sactipeptides. The distinguishing feature of this mechanism relative to those shown in Fig. S5 is formation of a reactive intermediate, such as a ketoimine, analogous to Dha or Dhb in the lantipeptide mechanism, which would be trapped from the re- or si-face to generate mixed regioselective outcomes.