Fig. 3.
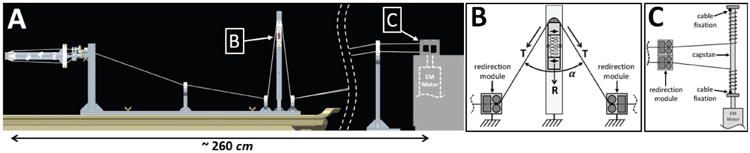
A: Side view CAD rendering of the cable transmission consisting of two closed-loop drives fed through a length/tension adjustment mechanism. For both DOF the cable is guided from the actuation system to the end-effector finger interface by 6 sets of cable redirection modules. Each redirection module consists of two horizontal pulleys on the side that copes with height changes, as well as two vertical pulleys on the side that copes with lateral deviation of the cables. B: Schematic of the length/tension adjustment mechanism: an MRI-compatible spring between two polymer sliding modules generates a force R, adjusting the cable tension T in the transmission. C: Schematic portraying the cable fixation on the two sides of the capstan which is attached to the motor shaft.
