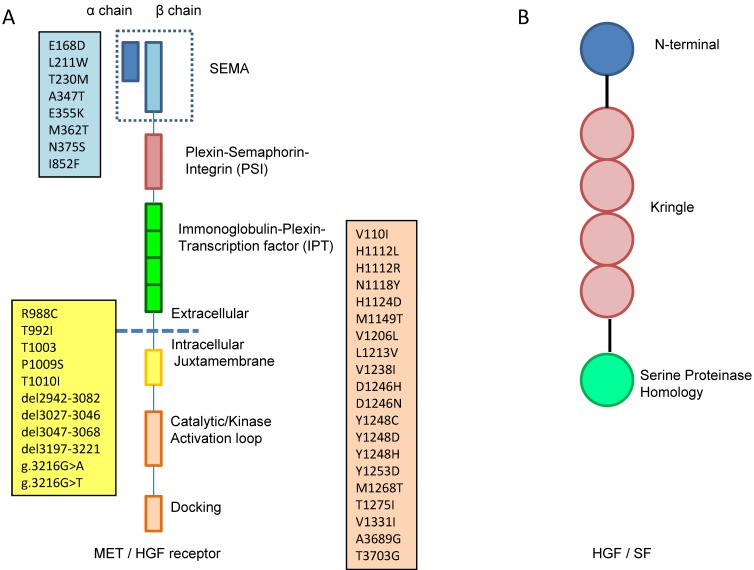
Figure 1.
A. MET is a disulfide linked heteroimeric RTK consisting of an extracellular α chain, a β chain that encompasses the remainder of extracellular domain, the juxtamembrane and the kinase domains. The extracellular component groups several domains including a large N-terminal semaphorin (Sema) domain (exon 2), a plexin-semaphorin-integrin (PSI) domain, and a stalk structure consisting of four immunoglobulin-plexin-transcription factor (IPT) domains. The intracellular component contains a juxtamembrane region (exon 14), a catalytic region with the enzyme activity, and a C-terminal region (exon 15-21) acting as a docking site for adaptor proteins. The locations of gene mutation are shown in the boxes, the blue box lists the locations of mutation in sema domain (exon2), the yellow box lists the locations of mutation in juxtamembrane (exon 14) and the pink box lists the locations of mutation in tyrosine kinase domain (exon15-21). B. HGF consists of six domains including an N-terminal domain, four kringle domains and a C-terminal domain which is a serine proteinase homology (SPH) domain.