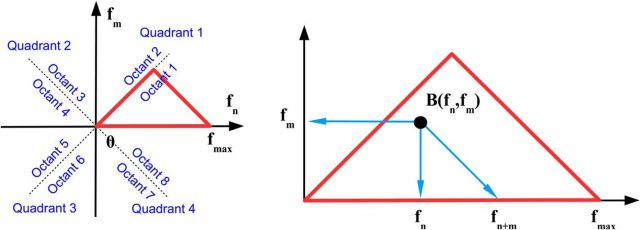
Figure 1.
Bispectral symmetries (see Eq. 7–9). Left, Quadrant and octants of the frequency plane. Red triangle represents the area containing nonredundant information for the DFT. Right, Peak in the bispectral estimate (represented by the black dot) represents a phase-coupled triplet (fn, fm, fn + m), where fn, fm are two frequencies in the Fourier representation sequence defined in Equation 1. If a bispectral peak (black dot) is on the first diagonal, then m = n, meaning that frequency fn is phase correlated to its second harmonic f2n = 2fn.