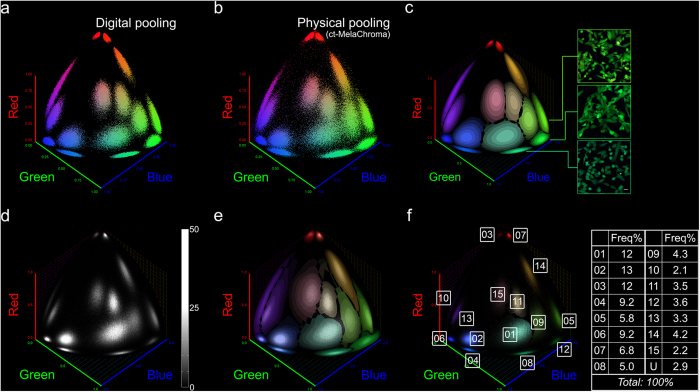
Figure 3. Generating clonally trackable MelaChroma and clonal assignment.
(a) Digitally pooled color data of a 15-clone subset selected from the MelaChroma candidate clonal pool. These fifteen clones had non-overlapping chromatic modes and 50% isosurface chromatic spreads. Color data of 9E4 cells represented each clone. Spherical scatter plot of the pooled color data is shown. (b) Spherical scatter plot of the cell population generated by physically pooling the fifteen clones in (a). We named this population ct-MelaChroma for its clonal trackability. 1.35E6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry two days after clonal pooling. (c) Chromatic landscape of ct-MelaChroma. Chromatic modes and chromatic spreads of the fifteen clones were positioned on this landscape by the digital pooling of clonal color data (a). Clonal assignment rules for chromaticity grid elements mapped to multiple clones were subsequently applied (Supplementary Fig. S10). Confocal images exemplify clones that were difficult to distinguish by eye but readily distinguishable by chromaticity plotting (scale bar: 25 μm). (d) Spherical histogram of ct-MelaChroma eight days post clonal pooling. ct-MelaChroma’s flow cytometry data carried no information of each cell’s clonal identity. 1.53E6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (e) Our clonal assignment algorithm numerically matched the chromaticity coordinate of each ct-MelaChroma cell to the chromaticity coordinates bounded by each clone in the chromatic landscape. An overlay of (d,c) illustrates this concept. Correction of non-ideal chromatic stability had been performed (Supplementary Fig. S11). (f) ct-MelaChroma’s clonal composition is the output of the clonal assignment algorithm. Cells in the spherical histogram (d) were color-coded according to their assigned clone. Numerical frequency of each participant clone was listed. “U” (unassigned) designated cells with out-of-bounds chromaticity coordinate in the chromatic landscape or cells that could not be exclusively assigned to one clone (“yellow” region, Supplementary Fig. S10).