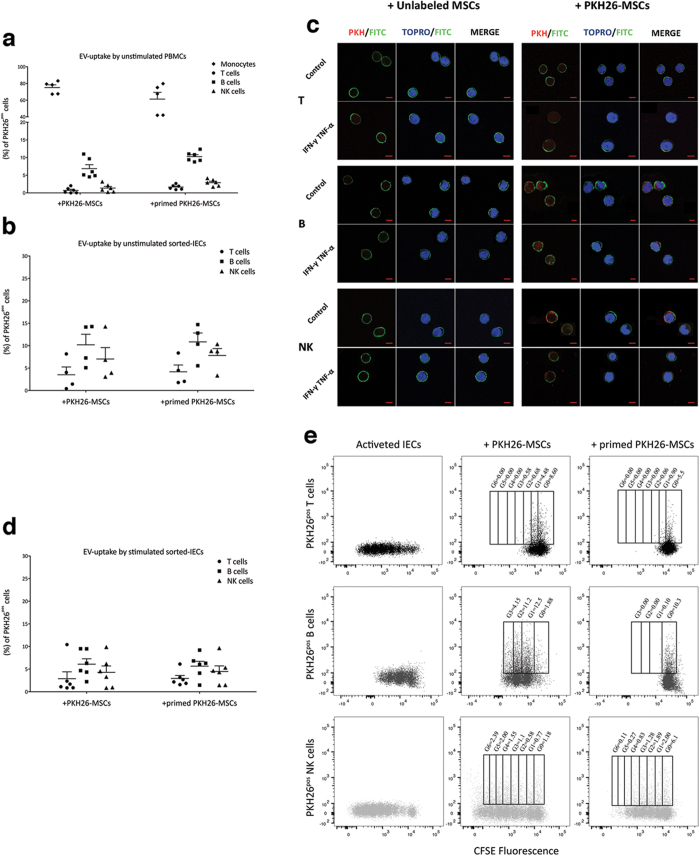
Figure 2. Internalization of MSC-derived EVs by IECs.
Resting and primed PKH26-MSCs were cultured in presence of unstimulated PBMCs or sorted-T, -B or -NK cells in order to assess the transfer of MSC-derived EVs to IECs. After 4 days, the cells were harvested and labeled with anti-CD45, anti-CD3, anti-CD14, anti-CD56, anti-CD19 to identify the different IEC lineage inside unfractionated PBMCs (a); anti-CD45 were used for sorted-IECs (b–e). TOPRO-3 was added to detect viable cells. The EV-uptake by IECs was detected as percentage of lineage specificpos/PKH26pos IECs by FACS. (c) Representative immunofluorescence staining of CD45pos/PKH26pos IECs. At the end of co-cultures, cells were detached and labeled with anti-CD45 (green) and TOPRO-3 (blue nuclei) to assess the incorporation of PKH26-EVs (red). Scale bars: 5 μm. Images were obtained by LSM 710 confocal microscopy (Zeiss) at 63x magnification. (d) EV-internalization by stimulated CFSE labeled IECs was evaluated after 6 days for T and NK cells and after 4 days for B cells. (e) CFSE plot representative of three independent experiments, showing the localization of EVs inside IEC generation as percentage of CFSEpos/PKH26pos IECs. Error bars represented mean ± SEM.