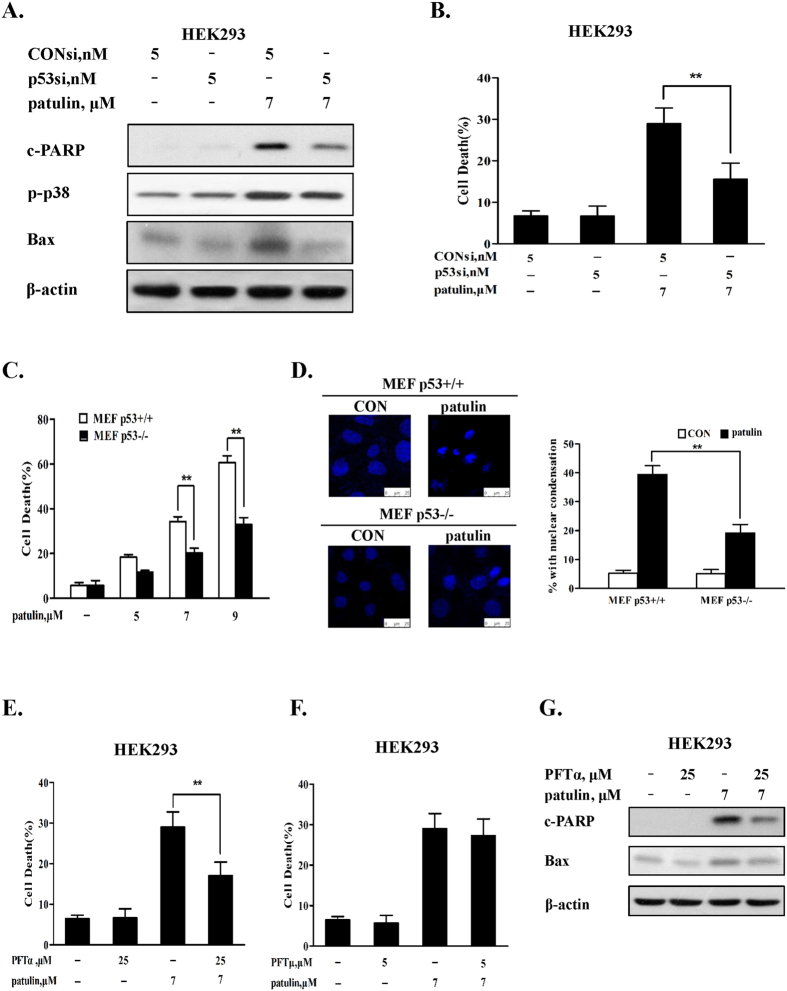
Figure 5. p53 exerted pro-apoptotic activity through a transcriptional mechanism.
(A). Effects of p53 inhibition by RNAi on patulin-induced Bax up-regulations, p38 phosphorylation and PARP1 cleavages. The cells were transfected with p53 siRNA using INTERFER siRNA transfection agent. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were treated with 7 μM patulin for 24 h and then Bax, p38 phosphorylation and PARP cleavages were analyzed by western blotting. (B). Effects of p53 knockdown on patulin-induced apoptosis. The cells were transfected with p53 siRNA using INTERFER siRNA transfection agent. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were treated with 7 μM patulin for 30 h and then apoptosis was measured by Annexin V staining. (C). Patulin induced apoptosis in p53 knockout/wild type MEF cells. The cells were treated with various patulin concentrations for 18 h and then apoptosis was measured by Annexin V staining. (D). PAT induced nuclear morphological changes in p53 knockout/wild type MEF cells. The cells were treated with 7 μM patulin for 12 h and then the nuclei were stained with DAPI. (E). Effects of p53 inhibitor pifithrin-α on patulin-induced apoptosis measured by Annexin V staining. (F). Effects of p53 inhibitor pifithrin-μ on patulin-induced apoptosis measured by Annexin V staining. (G). Effects of p53 inhibitor pifithrin-α on patulin-induced Bax up-regulations. The cells were treated with patulin in the presence or absence of pifithrin-α for 24 h and then Bax expression was analyzed by western blotting. n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (The blots shown are representative of three independent experiments).