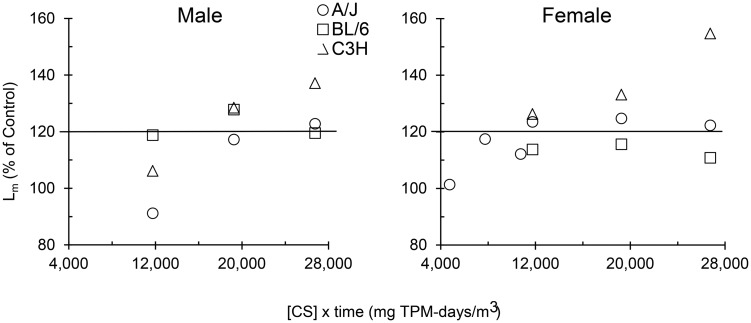
FIG. 4.
Comparison of CS-induced emphysema severity (measured by the mean linear intercept [Lm]) in 3 strains of mice relative to the CS dose that was calculated by multiplying CS concentration and exposure duration in mg total particulate material [TPM]-days/m3. Mean values are expressed as a percentage of duration-matched filtered air-exposed control means. Data used for the A/J mice were published previously (March et al., 2006), where mean percentages for females at 4750, 7750, and 10 750 mg TPM-days/m3 correspond to exposure at 100 mg TPM/m3 for 10, 16, and 22 weeks, respectively. Remaining values at 11 750, 19 250, and 26 750 mg TPM-days/m3 correspond to exposure at 250 mg TPM/m3 for 10, 16, and 22 weeks, respectively. The line at 120% of control represents a minimum for clinically significant abnormal air space enlargement in age-matched human lungs (Verbeken et al., 1992).