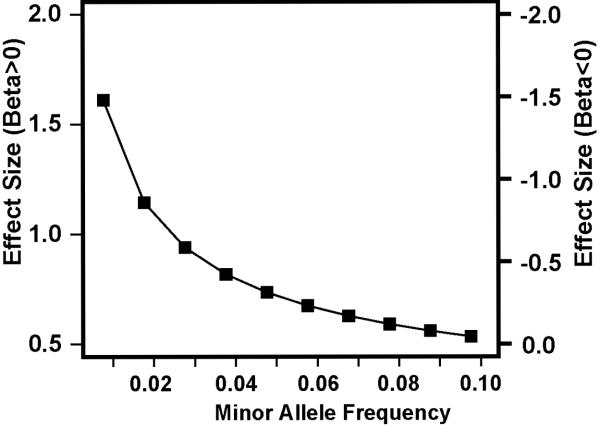
Fig 2. Power to detect genome-wide significant association with AD in the Framingham Heart Study.
Effect sizes (i.e., beta estimates in the regression model) to obtain 80% power for infrequent SNPs (0.01 ≤ minor allele frequency [MAF] ≤ 0.1) under the additive model were estimated using a sibling correlation of 0.199 in 2,779 relative pairs at the genome-wide significance level. Effect size of the SNP on AD risk (Y-axis) according to MAF (X-axis) was computed for rank-transformed liability scores. The power estimates are conservative because they account for only sib-pair relationships in the pedigree.