Abstract
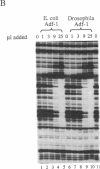
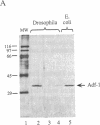
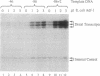
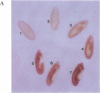
The Drosophila sequence-specific DNA binding protein, Adf-1, is capable of activating transcription of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene, Adh, and is implicated in the transcriptional control of other developmentally regulated genes. We have cloned the cDNA encoding Adf-1 by generating specific DNA probes deduced from partial amino acid sequence of the protein. Several cDNA clones encoding an extended open reading frame were isolated from a phage lambda library. The complete amino acid sequence of Adf-1 deduced from the longest cDNA reveals structural similarities to the putative helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif of Myb and Myb-related proteins. DNA sequence analysis of genomic clones and Northern blot analysis of mRNA suggest that Adf-1 is a single-copy gene encoding a 1.9-kb transcript. Purified recombinant Adf-1 expressed in Escherichia coli binds specifically to Adf-1 recognition sites and activates transcription of a synthetic Adh promoter in vitro in a manner indistinguishable from the protein purified from Drosophila. Temporally staged Drosophila embryos immunochemically stained with affinity-purified anti-Adf-1 antibodies indicate that Adf-1 protein is not detectable in very early embryos and does not appear to be maternally inherited. During later stages of embryogenesis, Adf-1 appears to be expressed in the nucleus of most somatic cells in the embryo with possibly higher concentrations found in some tissues.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benyajati C., Ayer S., McKeon J., Ewel A., Huang J. Roles of cis-acting elements and chromatin structure in Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7903–7920. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors and the control of Drosophila development. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Identification of cis-regulatory elements required for larval expression of the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):637–646. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. The role of specific enhancer-promoter interactions in the Drosophila Adh promoter switch. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2191–2120. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Holtzman D. A., Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Synergistic activation by the glutamine-rich domains of human transcription factor Sp1. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90606-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Systematic method for the detection of potential lambda Cro-like DNA-binding regions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England B. P., Heberlein U., Tjian R. Purified Drosophila transcription factor, Adh distal factor-1 (Adf-1), binds to sites in several Drosophila promoters and activates transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5086–5094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Drosophila Adh: a promoter element expands the tissue specificity of an enhancer. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Leutz A., Gibson T., Graf T. DNA-binding domain ancestry. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):134–134. doi: 10.1038/342134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., de Blaquiere J. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones of the murine myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2003–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., Tjian R. Temporal pattern of alcohol dehydrogenase gene transcription reproduced by Drosophila stage-specific embryonic extracts. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):410–415. doi: 10.1038/331410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju Q. D., Morrow B. E., Warner J. R. REB1, a yeast DNA-binding protein with many targets, is essential for growth and bears some resemblance to the oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5226–5234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Isolation of the proto-oncogene c-myb from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockett T. J., Ashburner M. Temporal and spatial utilization of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene promoters during the development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Castro M. M., Aboul-ela F., Tinoco I., Jr Base pairing involving deoxyinosine: implications for probe design. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8927–8938. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. H., Martin-Blanco E., Coleman K. G., Poole S. J., Ellis M. C., Kornberg T. B., Goodman C. S. Expression of engrailed proteins in arthropods, annelids, and chordates. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):955–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90947-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Admon A., Patel N., Tjian R. The Drosophila Fos-related AP-1 protein is a developmentally regulated transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):822–834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. A., Wakimoto B. T., Subers E. M., Nathanson N. M. Characterization and functional expression in mammalian cells of genomic and cDNA clones encoding a Drosophila muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9039–9043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofer W., Martin P. F. Analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:203–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streck R. D., Macgaffey J. E., Beckendorf S. K. The structure of hobo transposable elements and their insertion sites. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3615–3623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., McAllister L., Goodman C. S. Sequence analysis and neuronal expression of fasciclin I in grasshopper and Drosophila. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90574-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]