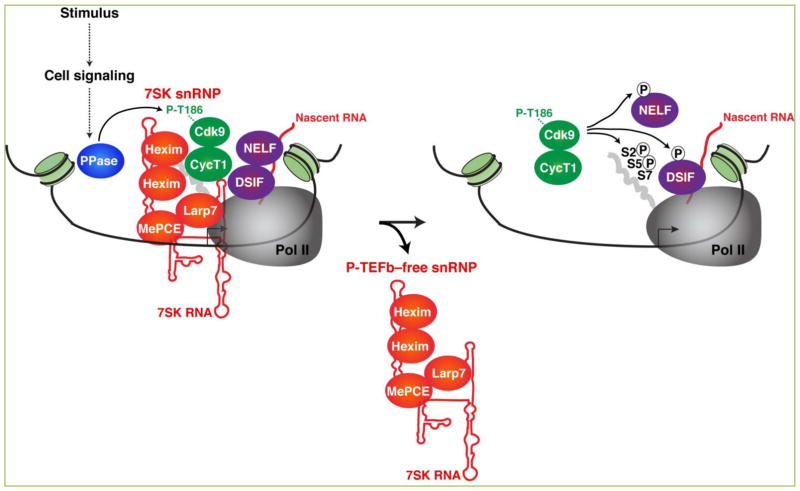
Figure 3. P-TEFb dissociation from the 7SK snRNP by the action of phosphatases promotes transcriptional pause release.
In response to intrinsic/extrinsic stimulus, cell-signaling cascades are activated, and phosphatases (PPase) are induced to promote Cdk9 T-loop dephosphorylation (P-T186) causing P-TEFb release from the 7SK snRNP complex. However, it remains unclear whether the PPases function on or off chromatin (or both). Released P-TEFb can then phosphorylate the Pol II CTD on Ser5 (S5) and Ser2 (S2) residues, DSIF (which is converted into a positive elongation factor), and NELF (which is evicted from Pol II) thereby relieving Pol II stalling at promoter-proximal regions. Upon 7SK snRNP disassembly, the P-TEFb free snRNP is repositioned in the promoter-proximal region or dislodged from chromatin. This aspect of the model requires further investigation (see the text for details). The arrow indicates the position of the TSS.