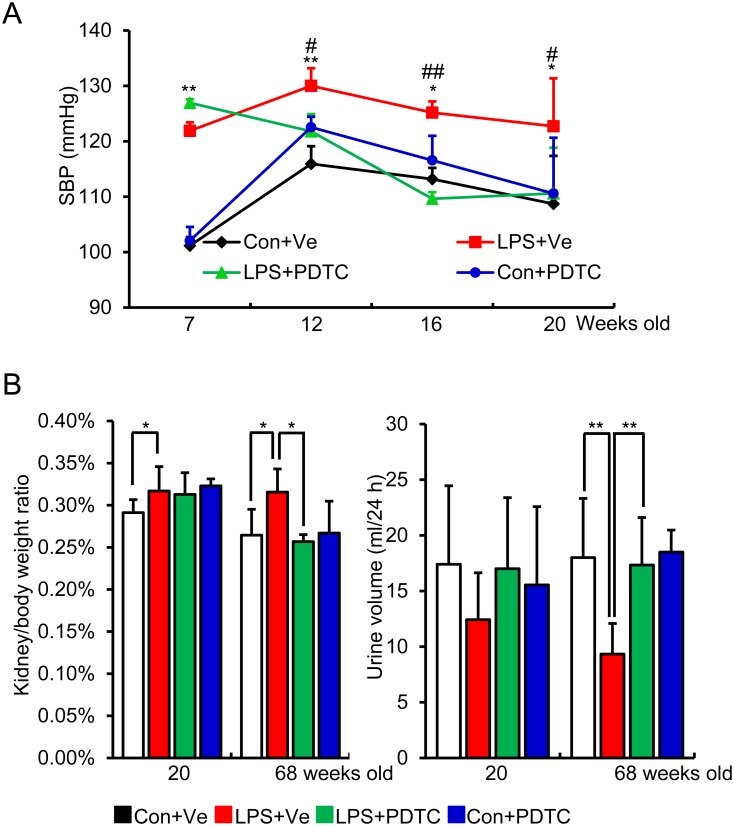
Fig 2. Post-natal inhibition of NF-κB activity by PDTC prevents blood pressure elevation (A), reverses the increased kidney/body weight ratio (B) and the reduced 24 hour urine volume (C).
Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was measured by a noninvasive tail-cuff method at indicated time points after PDTC treatment (A). Relative kidney weight was calculated as a ratio of kidney wet weight to whole body weight after animals were sacrificed at indicated time-point (B). 24 hour urine volume was calculated by collecting urine for 24 hour by using metabolic cage at the indicated time-point (C). Data are presented as mean ± SD. n = 16 offspring for each group for (A, B, C).*P<0.05 or **P<0.01, Con+Ve vs LPS+Ve; #P<0.05 or ##P<0.01, LPS+PDTC vs LPS+Ve (A); * and ** indicate P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively, which denote statistical comparison between the two marked treatment groups (B, C) (Two-way ANOVA followed by LSD test for inter-group comparison (A) or Dunnett T3 test (B and C) for inter-group comparison). Indications of Con+Ve, LPS+Ve, LPS+PDTC and Con+PDTC are as described in Fig 1.