Fig 6. M. tuberculosis converts normal-density granulocytes (NDGs) to low-density granulocytes (LDGs).
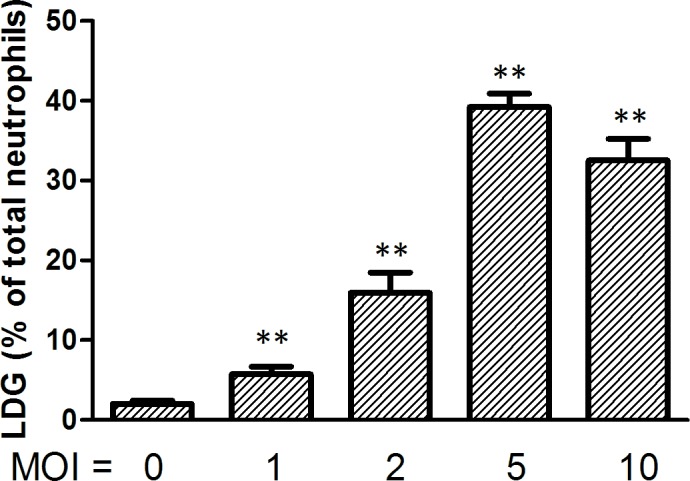
Neutrophils were isolated from the erythrocyte fraction of healthy volunteers and in vitro challenged with M. tuberculosis H37Rv at the indicated MOI for 4 h. Cells were then washed once, resuspended in 3 ml sterile saline and added to 3 ml of autologous uninfected whole blood. LDGs in this mixture and uninfected venous blood were counted by flow cytometry following discontinuous density gradient centrifugation. The number of LDGs in infected neutrophils was calculated by subtracting the number of LDGs in uninfected blood from LDGs in the mixture, and the percentages of LDGs to total infected neutrophils were calculated and displayed. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by comparison with the uninfected group by a one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test. **P < 0.01.
