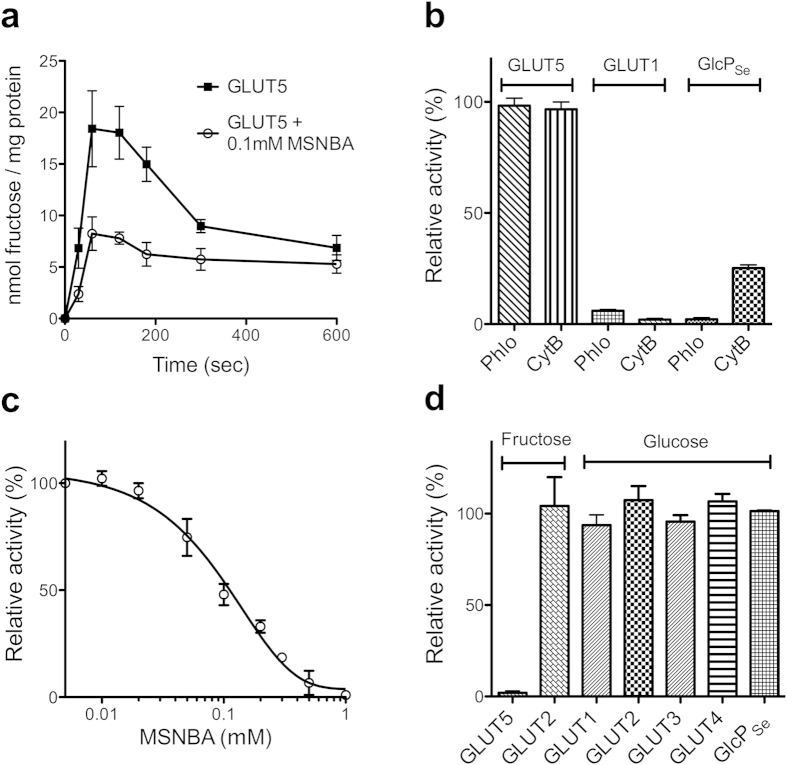
Figure 1. Effect of MSNBA on human GLUT1-5 and GlcPSe transport activities.
(a) Fructose entrance counter-flow transport in GLUT5 proteoliposomes, in the absence (filled squares) and presence (empty circles) of 0.1 mM MSNBA. Transport was initiated by the addition of GLUT5 proteoliposomes to the reaction solution containing 10 μM C14-fructose and stopped at the indicated time points. (b) Effect of common GLUT1 inhibitors on the relative transport activity of GLUT5, GLUT1 and GlcPSe. Glucose (for GLUT1) or fructose (for GLUT5) entrance counter-flow transport was measured one minute after initiation of transport by adding proteoliposomes to assay solution containing 10 μM C14-hexose and 2 mM phloretin (Phlo) or cytochalasin B (CytB). Glucose uptake for GlcPSe was measured one minute after initiation of transport with 30 μM C14-glucose in the presence of 2 mM phloretin or cytochalasin B in right-side-out vesicles. (c) Dose-dependent MSNBA inhibition of GLUT5 fructose transport in proteoliposomes. Each point was measured one minute after transport initiation, using the entrance counter-flow transport assay. IC50 of MSNBA inhibition was 0.10 ± 0.03 mM. Curve was calculated with Prism (GraphPad Software). (d) Effect of 2 mM MSNBA on the fructose transport by GLUT5 or GLUT2 or glucose transport by GLUT1-4 or GlcPSe. GLUT1-5 transport activity was measured in proteoliposomes, using the entrance counter-flow assay, as in (b). GlcPSe glucose transport was measured in right-side-out vesicles as in (b). Error bars represent standard deviations from 3 different experiments (a–d).