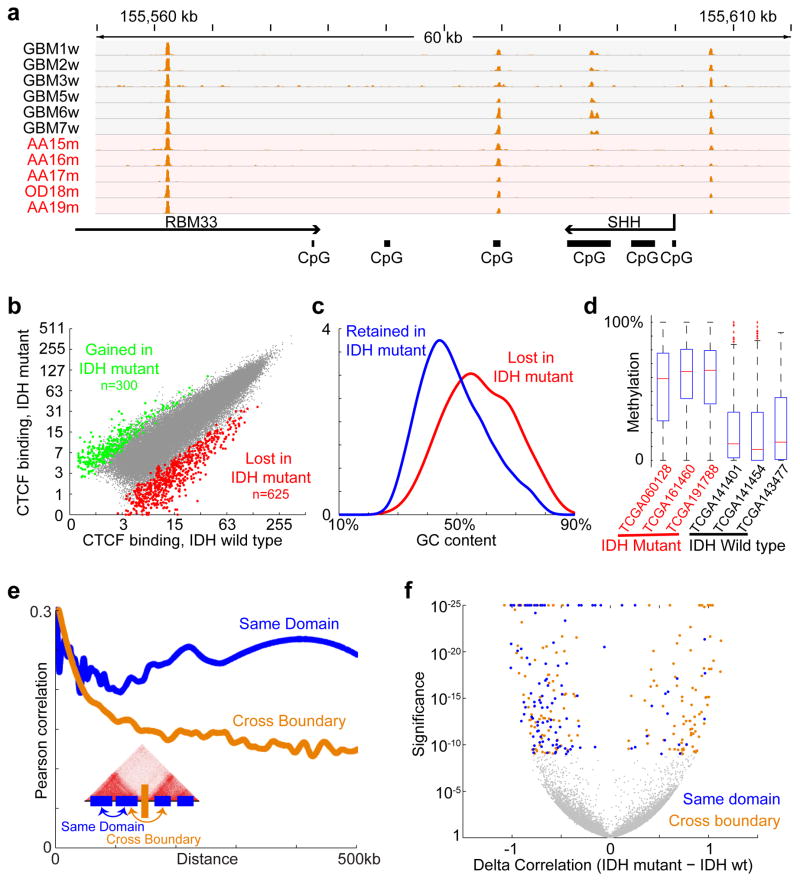
Figure 1. CTCF binding and gene insulation compromised in IDH mutant gliomas.
(a) Binding profiles for the methylation-sensitive insulator CTCF are shown for a representative locus in IDH1 mutant and wildtype tumors, normalized by average signal. (b) Scatterplot compares CTCF binding signals between IDH mutant (y-axis) and IDH1 wildtype gliomas (x-axis) for all detected CTCF sites. A larger fraction of sites is commonly lost in all IDH1 mutants (n=625) than gained (n=300). (c) Histogram compares GC content between CTCF sites that are lost or retained. (d) Box plots show DNA methylation levels over lost CTCF sites, as determined from whole genome bisulfite data for three IDH wildtype and three IDH mutant tumors. (e) Plot depicts average correlation between gene pairs as a function of distance across RNA-seq profiles for human brain20. Gene pairs separated by a constitutive CTCF-bound boundary per HiC15 have lower correlations. (f) Volcano plot depicts the significance (y-axis) of gene pairs that are more (or less) correlated in IDH mutant than IDH wildtype lower-grade gliomas. Gene pairs with significantly increased correlations in IDH mutants (right) tend to cross boundaries (orange), while those with decreased correlations (left) more likely reside in the same domain (blue). These data indicate that IDH mutant, G-CIMP gliomas have reduced CTCF binding and altered expression patterns suggestive of defective gene insulation.