Figure 4.
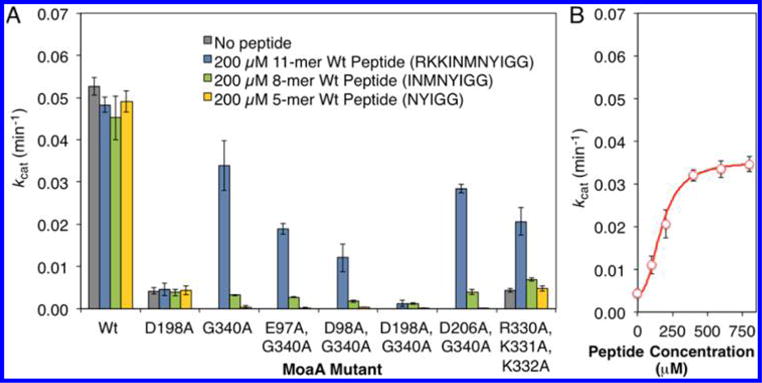
Investigation of the peptide binding site. (A) Activity of MoaA variants with mutations in the putative C-terminal tail interaction interface residues. The activity was determined by the MoaA/MoaC coupled assay in the absence (gray bar), or in the presence of the 11-mer (blue bars), 8-mer (green), or 5-mer (yellow) wt peptide (200 μM). (B) Activity of R330A/K331A/K332A-MoaA in the presence of specified concentrations of the 11-mer wt peptide. The activity was determined by the MoaA/MoaC coupled assay. The solid line is the nonlinear fit to Hill equation19 with kcat = 0.035 min−1, Kd = 172 μM, and Hill coefficient = 2.46. Rescue of the R330A/K331A/K332A-MoaA activity by the 11-mer peptide with Kd comparable to the rescue of G340A-MoaA provides strong evidence that the R330/K331/K332 residues are critical for the binding of the peptide as well as the C-terminal tail. All experiments were at least triplicated, and error bars represent standard deviation.
