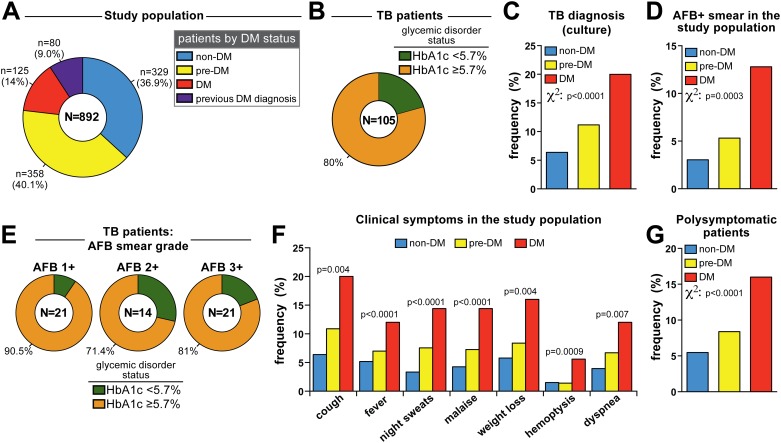
Fig 2. Glucose metabolism disorder is associated with TB in patients with respiratory symptoms.
(A) Stratification of patients presenting with respiratory symptoms based on HbA1c levels. (B) Frequency of abnormal HbA1c levels in patients diagnosed with pulmonary TB. (C) Frequency of TB cases in patients without previous DM diagnosis who were classified in non-DM, pre-DM and DM based on Hb1Ac. (D) Frequency of AFB+ in sputum smears from the entire study population. (E) Frequency of TB patients with different AFB smear grades in sputum classified according to altered HbA1c levels. (F) Prevalence of TB-related symptoms relative to the study population was compared between non-DM, pre-DM and DM TB patients without previous DM diagnosis. (G) Individuals were further categorized in polysymptomatic (> 3 symptoms) or non-polysymptomatic (≤ 3 symptoms). In (C), (D), (F) and (G), data were compared using the chi-square test.