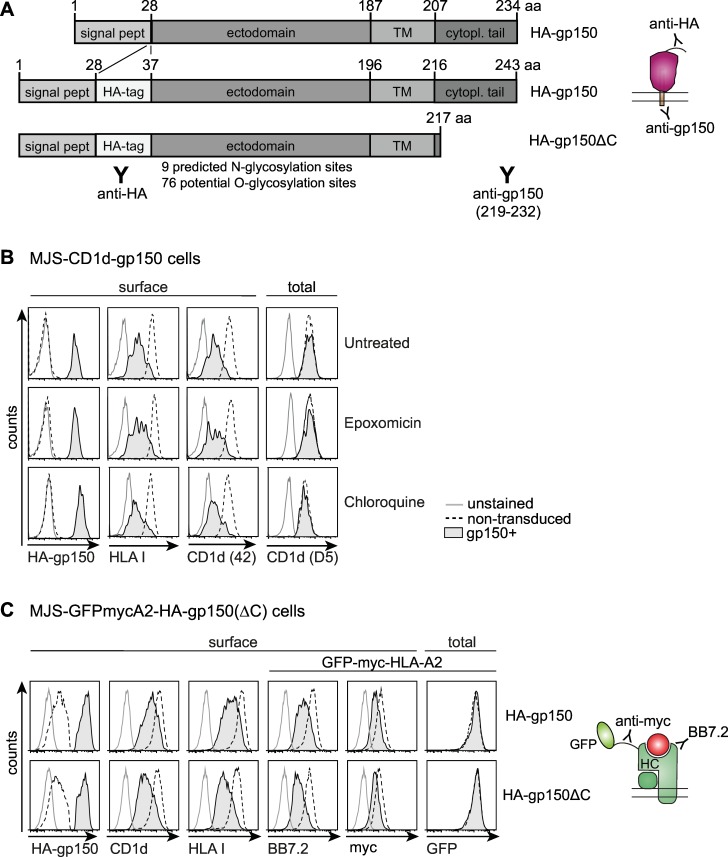
Fig 4. Immune evasion by EBV gp150 does not depend on degradation of Ag-presenting molecules nor on gp150’s cytoplasmic tail.
A) Schematic overview of the gp150 constructs and Abs used. Signal peptide, transmembrane domain, and cytoplasmic tail are abbreviated as signal pept, TM, and cytopl tail, respectively. B) Three days after lentiviral transduction, MJS-CD1d-gp150 cells were cultured overnight in the presence of an inhibitor of proteasomes (15nM epoxomicin) or of endolysosomal proteolysis (25μM chloroquine). Subsequently, flow cytometry was used to determine surface levels of HA-tagged gp150 (HA-gp150; detected with anti-HA Ab), HLA I, and mature CD1d (Ab #42) complexes on non-permeabilized cells and intracellular staining was performed to detect immature CD1d (Ab D5) molecules in permeabilized cells. C) MJS-GFPmycA2 cells were transduced with a lentivirus encoding HA-gp150 (upper) or HA-gp150ΔC (lower). Cell surface levels of CD1d, HLA I, and HLA-A2 (BB7.2 and anti-myc tag) and total HLA-A2 (GFP) levels were compared for gp150- and gp150+ cells.