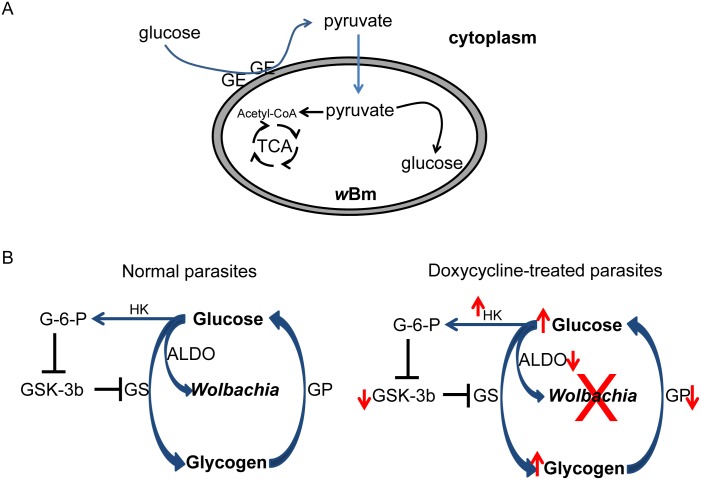
Fig 6. Schematic representation of the role wBm may play in regulating the metabolism of glucose and glycogen in B. malayi.
(A) wBm require pyruvate for intracellular glucose and energy production. Parasite glycolytic enzymes (GE) are clustered to the bacterial surface in a complex with wBm00432, which can support the conversion of the intracellular glucose into pyruvate. Pyruvate is then utilized by the bacteria either for energy production or gluconeogenesis. (B) Bacteria change the expression of host genes that are involved in the glycogen metabolic pathway. A decline in bacterial fitness due to antibiotic treatment increases glucose levels and decreases utilization of glycogen, resulting in an increase in glycogen stores as well. Abbreviations: TCA: tricarboxylic acid cycle, GS: glycogen synthase, GP: glycogen phosphorylase, GSK-3: glycogen synthase phosphatase-3, HK: hexokinase, G-6-P: glucose-6-phosphate.