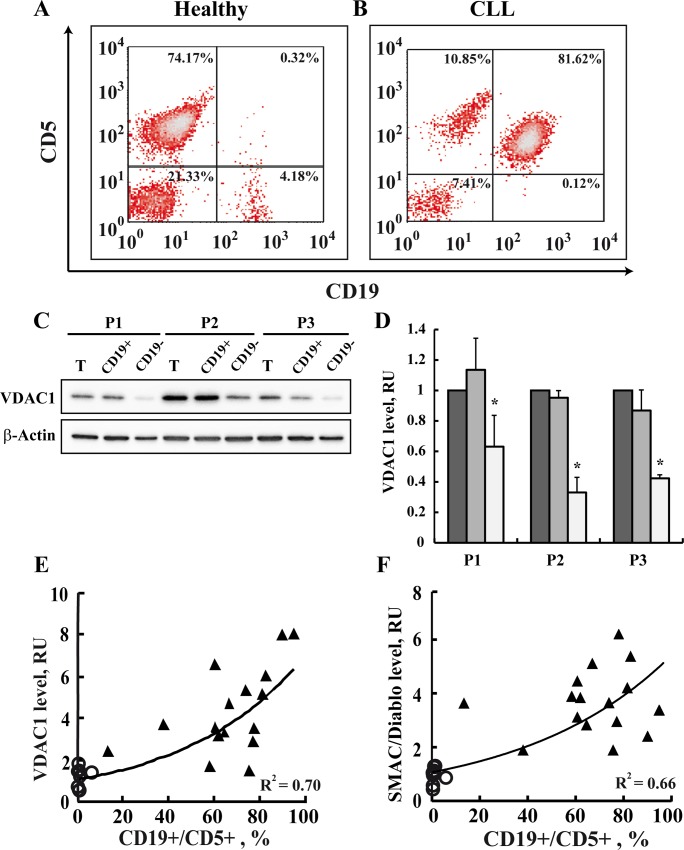
Fig 5. The VDAC1 expression level is correlated with the level of cancerous CD19+/CD5+ cells and apoptosis-related proteins.
The percentages of CD19+/CD5+ cells in PBMCs isolated from representative healthy donor (n = 9) (A) or CLL patient (n = 16) (B) were determined using monoclonal antibodies directed to CD19/CD5, by flow cytometry analysis. CD19+/CD5+ cells represent cancerous CLL B lymphocytes. PBMCs obtained from 3 CLL patients (P (were subjected to CD19-positive cell separation using a magnetic bead-based method described in Materials and Methods. VDAC1 levels in PBMCs and their CD19-positive and -negative fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-VDAC1 antibodies (C). Quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM) (D) is presented. VDAC1 (E, R2 = 0.7) and SMAC/Diablo (F, R2 = 0.66) expression levels were determined as a function of the percentage of CD19+/CD5+ cells for each healthy donor (O) and CLL patient (▲). VDAC1 levels were assayed as described in the legend to Fig 3.