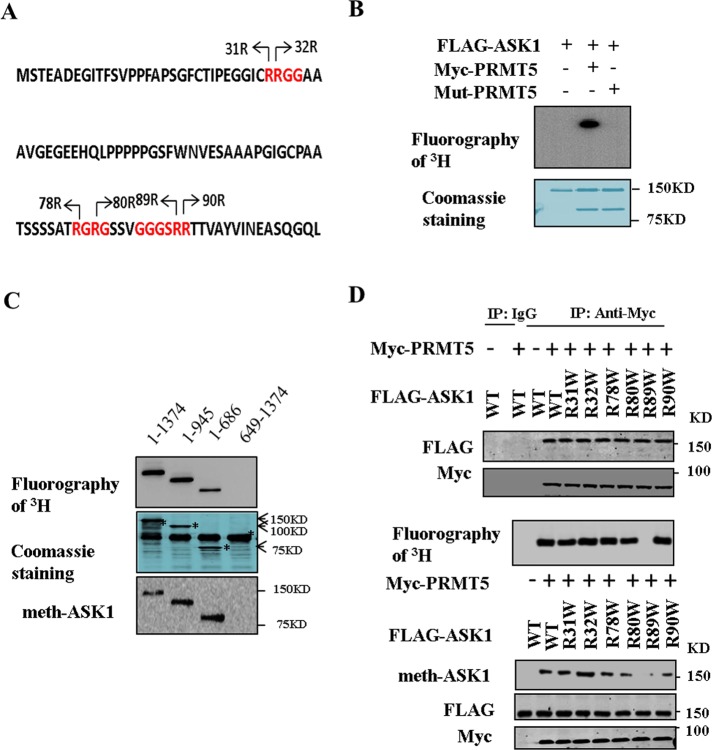
FIGURE 3:
PRMT5 methylates ASK1 at Arg-89. (A) The N-terminal sequence of human ASK1. RG-rich residues are in red, and potential methylation sites are indicated by arrows. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected for 48 h with expression vectors encoding FLAG-ASK1 or wild-type or mutant PRMT5. Purified FLAG-ASK1 and wild-type or mutant PRMT5 incubated in the presence of [3H]SAM. Reaction products were analyzed by fluorography. (C) Wild-type or mutant fragment ASK1 (5 μg) and Myc-PRMT5 (10 μg) incubated in the presence of [3H]SAM. Reaction products were analyzed by fluorography. The gel was also stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected for 48 h with expression vectors encoding FLAG-ASK1, mutant of ASK1, and Myc-PRMT5 as indicated. Cell lysates were then subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc or control IgG and then separated by 8% SDS–PAGE (top). Wild-type or mutant ASK1 and Myc-PRMT5 incubated in the presence of [3H]SAM. Reaction products were analyzed by fluorography (middle). Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot and examined by immunoblot with anti–dimethylation symmetric, anti-FLAG, and anti-Myc antibodies (bottom).