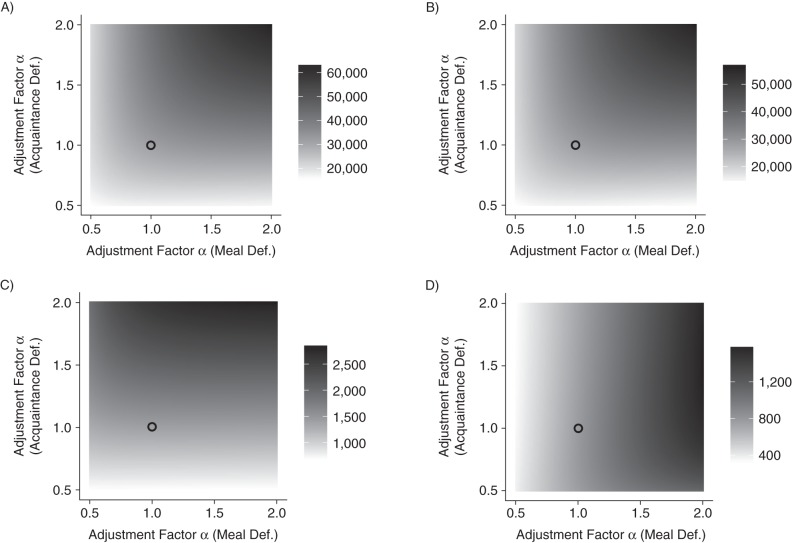
Figure 5.
Sensitivity of blended estimates of the sizes of 4 key hidden populations at risk of human immunodeficiency virus infection (female sex workers (A), clients of female sex workers (B), men who have sex with men (C), and people who inject illicit drugs (D)), Rwanda, 2011. Adjustment factor values (α) for the estimator from the meal definition of a social tie (x axis) and the estimator for the acquaintance definition of a social tie (y axis) were combined to produce a blended estimate. α can be written as the product of 4 terms related to reporting accuracy and network structure; α satisfies Areas with darker shading correspond to combinations of α values that lead to higher estimated group sizes. The circle shows the point estimate from Figure 4, which assumes that both the meal and the acquaintance definitions produce unbiased estimates.