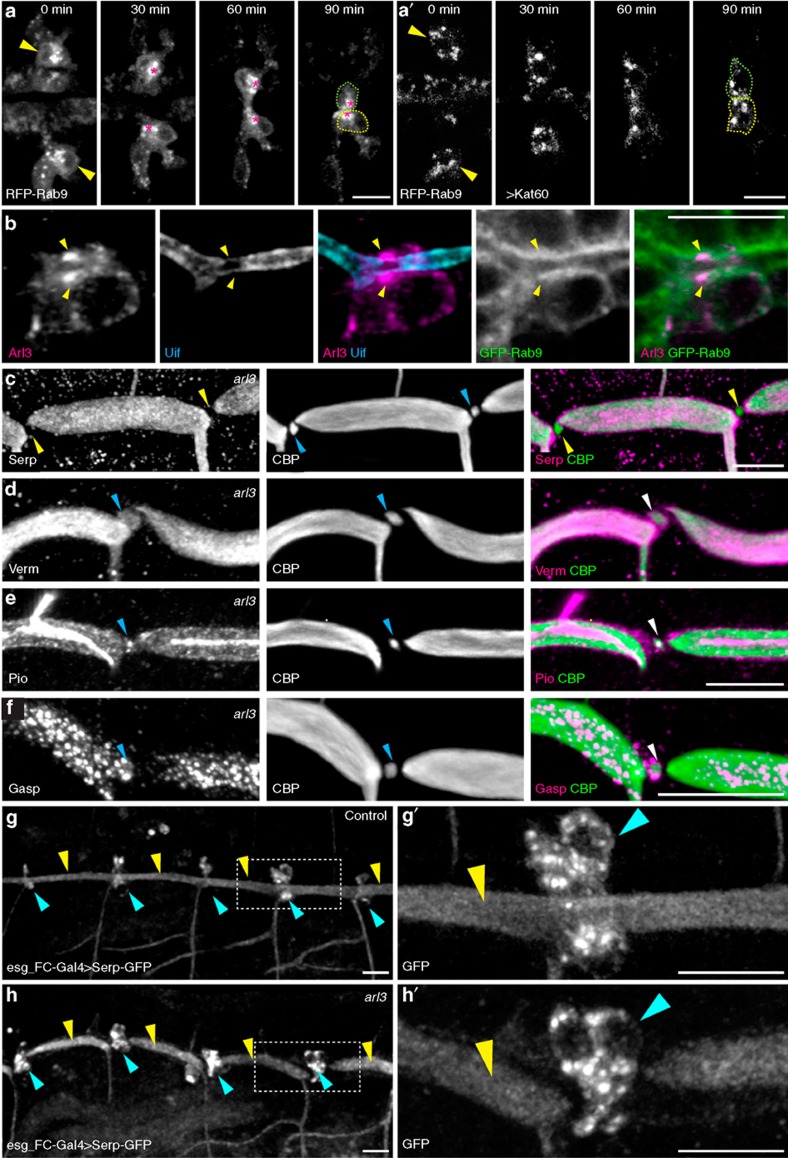
Figure 6. RFP-Rab9 vesicle trafficking in dorsal-branch FCs.
(a) In dorsal-branch FCs (indicated by arrowheads and dotted outlines), RFP-Rab9 vesicle clusters (asterisks) were localized near the FC contact site. Anterior, left. (a') Clustering of RFP-Rab9 vesicles was inhibited when microtubule was disrupted by Kat60. (b) Arl3 was also concentrated adjacent to the apical cell membrane (labelled with Uif) and co-localized with GFP-Rab9 at the FC contact site of the dorsal trunk (yellow arrowheads). (c–f) A specific secretion defect in arl3-mutant embryos: fusion points of stage-16 dorsal trunk were stained for CBP and Serp (c), Verm (d), Pio (e) or Gasp (f). Chitin, Verm, Pio and 2A12 were present in the lumen isolated from the FC contact site (blue arrowheads), whereas Serp (yellow arrowheads) was missing. (g,h) Test of directed Serp trafficking: Serp-GFP was expressed in FCs (blue arrowheads) using the esg_FC-Gal4 driver in control (arl31/+, g) and arl31 mutant (h) embryos, respectively. Secreted Serp-GFP was present throughout the lumen in control embryos (yellow arrowheads in g) but absent from the FC contact site in arl31 embryos (blue arrowheads in h). (g', h') Enlargement of the boxed regions in g and h, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm.