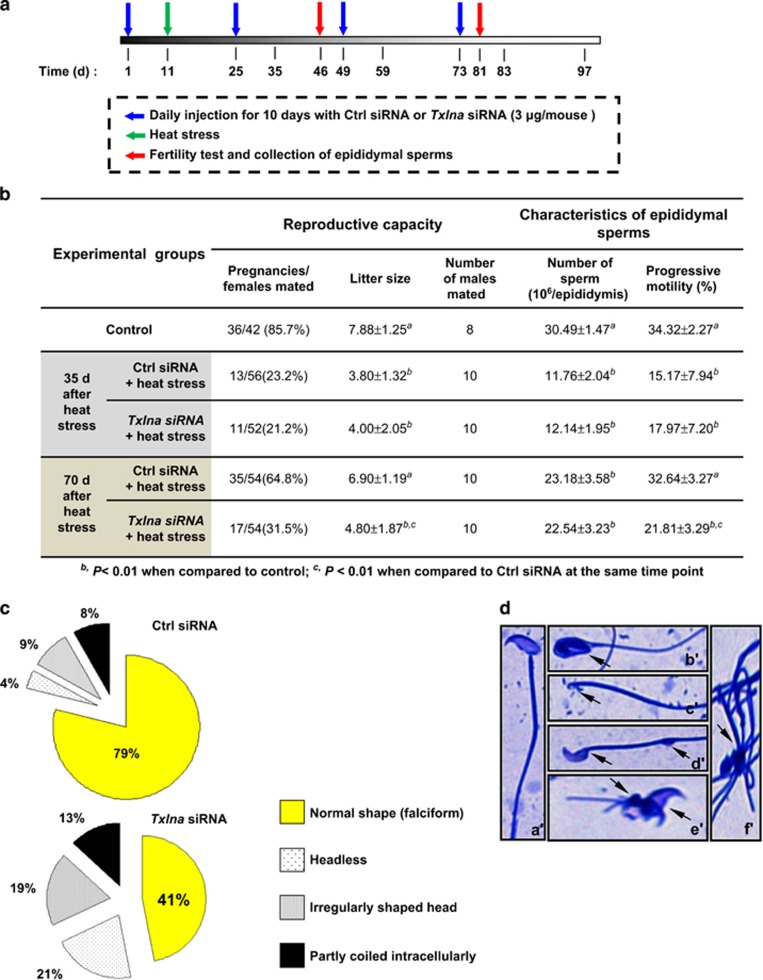
Figure 4.
Consequences of in vivo knockdown of Txlna in mouse testicular recovery after heat stress. (a) Schematic representation of the experimental procedure used in the in vivo study. In vivo siRNA for ablation of endogenous Txlna in testis was carried out as described above, followed by a 14-d break. Mice received four cycles of in vivo siRNA treatment. At 35 or 70 d after heat treatment, mice were killed. Fertility test and assessment of epididymal sperms were carried out as described in Materials and Methods (b). (c) Pie charts showing multiple sperm types and shapes in Ctrl siRNA or Txlna siRNA-treated mice 70 d after heat treatment. Two hundred sperm cells were analyzed for each genotype. (d) Representative examples of abnormal morphology of sperm from Txlna siRNA-treated mice at 70 d after heat stress. a′, normal sperm; b′, amorphous forms of head; c′, head loss; d′, lack of the usual hook; e′, folded tail; f′, bundled tails. Arrows indicate morphological abnormalities