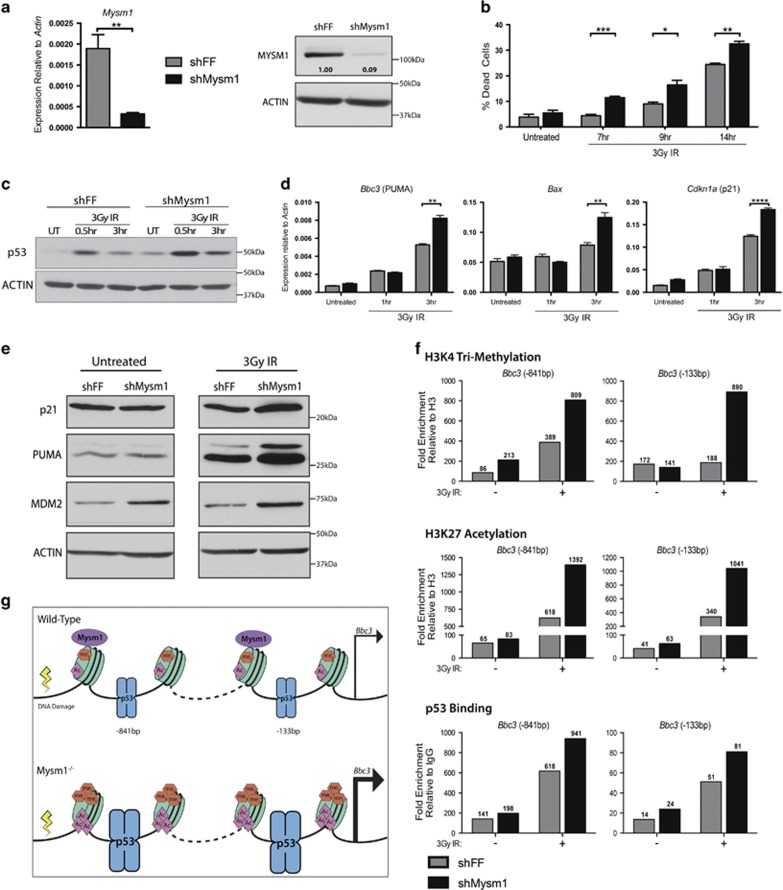
Figure 3.
MYSM1 regulates p53-target gene expression in hematopoietic progenitors. (a) Validation of reduced Mysm1 transcript and protein levels in the Mysm1-knockdown Ba/F3 hematopoietic progenitor cells (shMysm1, black bars), relative to control lines expressing shFF (gray bars). Gene expression normalized to Actin. (b) Measurement of cell death in Ba/F3 cells at 7, 9, and 14 h following 3-Gy irradiation. (c) Immunoblot showing levels of total p53 protein with ACTIN-loading control following irradiation. (d) Expression of p53-stress-response genes in knockdown shMysm1 cells and control shFF cells over a 3-h time course following 3-Gy irradiation. Normalization against Actin expression. (e) Immunoblots showing protein levels of p21, PUMA, MDM2, and ACTIN-loading control in knockdown shMysm1 and control shFF cells at a steady state and following 3-Gy irradiation. All data in a–e are representative of three independent shMysm1 and shFF lines. Bars in a, b, d represent mean±S.E.M.; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 using Student's t-test. (f) Effects of MYSM1 on chromatin modification and p53 recruitment to the Bbc3/PUMA gene promoter in untreated and 3-Gy-irradiated cells (3 h). Fold enrichment of histone H3K4 tri-methylation (H3K4me3), histone H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac), and p53 at the Bbc3/PUMA promoter in Mysm1 knockdown (shMysm1) and control (shFF) Ba/F3 cells analyzed using ChIP-qPCR. Enrichment values (shown above each bar) were calculated relative to control IgG for p53, and relative to total histone H3 for the histone marks using Pomc as a negative genomic region. Genomic structure of the locus with target primer sites is provided in Figure 2a. Data are representative of two independent experiments, with extra replicates in Supplementary Figure S3c. (g) Schematic summary of mechanism: MYSM1 antagonizes p53-induced Bbc3/PUMA gene expression in hematopoietic progenitors by inhibiting p53 recruitment and chromatin modification (H3K4me3 and H3K27ac)