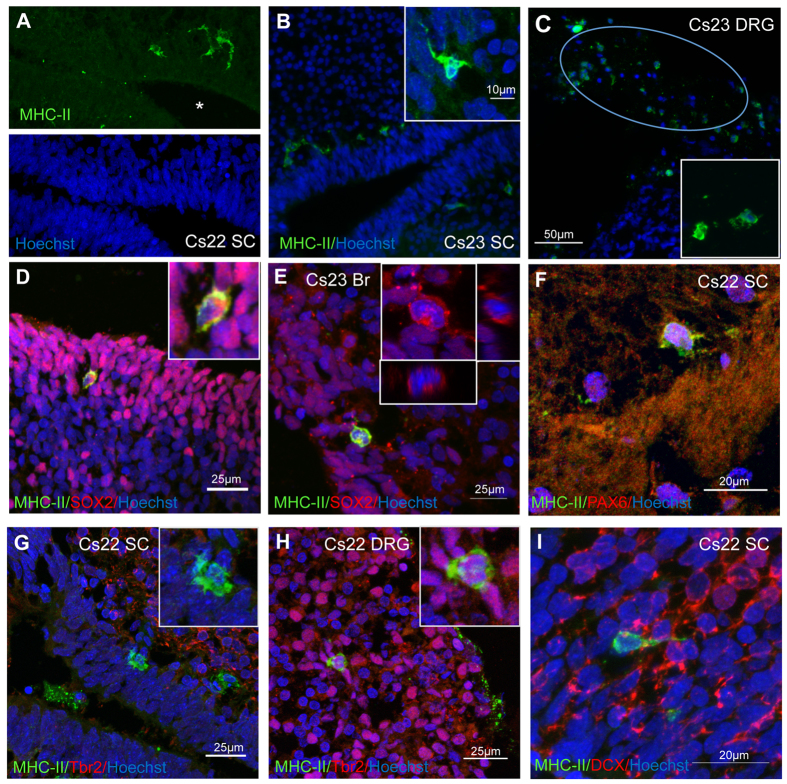
Figure 2. Detection of MHC class II and neural markers in human fetal CNS by immunofluorescence.
(A–C) MHC-II staining in spinal cords (SC) and dorsal root ganglion (DRG) from developing embryos at Carnegie stages 22 (Cs22) and 23 (Cs23). Note expression of MHC-II protein in a subset of cells in the germinal layer surrounding the central canal. The dorsal root ganglion, indicated by the oval in (C) contains several MHC-II-positive cells. The inserts show a group of positive cells at a higher magnification. (D,E) Double-staining for MHC-II and SOX2 in Cs23 spinal cords (D) and brain (E). MHC-II staining is detected in cells expressing SOX2 mainly in the cytoplasm (insert). (F) Spinal cord stained for PAX6 and MHC-II at higher magnification. PAX6 protein expression is detected in MHC-II positive cells. (G,H) Double-staining for Tbr2 and MHC-II protein expression in spinal cord (G) and DRG (H); note the absence of co-labelling in spinal cord cells, but co-expression in MHC-II positive cells in DRG. (I) Cs22 spinal cord stained for MHC-II and doublecortin (DCX) proteins; no double-labelled cell is detected.