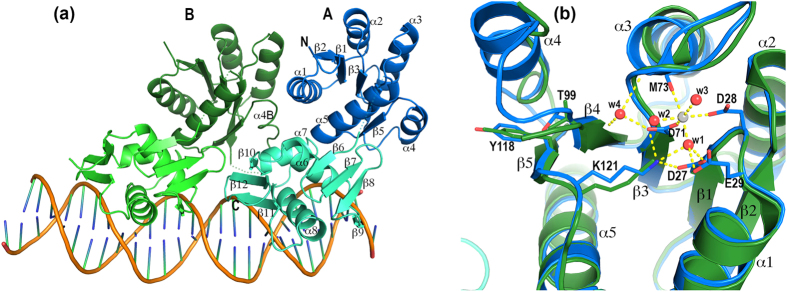
Figure 1. Structure of the PhoP-DNA complex.
(a) Ribbon diagram of the PhoP-DNA complex showing a tandem PhoP dimer binding to a direct-repeat DNA sequence. The two PhoP subunits are designated A and B, with subunit A binding to the first TCACAGC motif of the direct repeat and B to the second motif. Each domain of PhoP is coloured individually as follows: blue and cyan for the subunit A RD and DBD, respectively, and dark green and light green for subunit B. Secondary structural elements are labelled on subunit A. Helix α4 is unwound in subunit B and is labelled α4B. The sequence-recognition helix α8 is inserted into a major groove to contact the bases in the TCACAGC motif, whereas the wing interacts with the downstream minor groove. Dotted lines indicate residues that are disordered in the crystal structure. (b) Structural alignment of the two subunits around the phosphorylation site. Subunit A is coloured in blue and B is in green. A Ca2+ ion is found near the phosphorylation acceptor Asp71 with hexa-coordination as follows: two ligands from the Asp71 and Asp28 side chains, one from the carbonyl of Met73, and three from ordered water molecules. Side chains involved in coordinating the Ca2+ ion are shown only for the subunit A. The side chains of Thr99, Tyr118, and Lys121 are shown for both subunits.