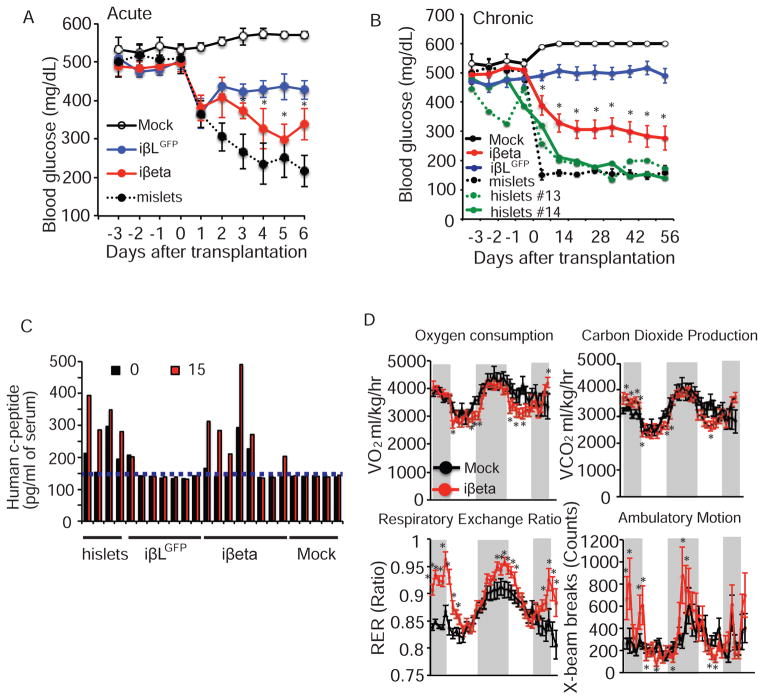
Figure 6. iβeta cells restore glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice.
(A) Acute effects on ad lib fed blood glucose levels in STZ-induced hyperglycemic NOD-SCID mice after mock transplantation (n=3), transplantation of iβLGFP cells (n=8), iβeta cells (n=7) and mouse islets (n=5). (B) Chronic effects on ad lib fed blood glucose levels of mock transplantation (n=3), transplantation of iβLGFP cells (n=14/12; 2 mice died 2 wks after transplantation), iβeta cells (n=13), mouse islets (n=5) and human islets (n=2). (C) Human c-peptide levels before and 15 minutes after a glucose challenge (2g/kg) in mice 2 months after the indicated transplantation (c-peptide ELISA limit of detection indicated by dotted line). (D) Oxygen consumption (VO2), carbon dioxide production (VCO2), Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER), and ambulatory motion of STZ treated NOD-SCID mice 56 days after mock (n=4) or iβeta cell transplantation (mice with blood glucose levels <250mg/dL, n=4). See also Figures S6 and S7.