Figure 1.
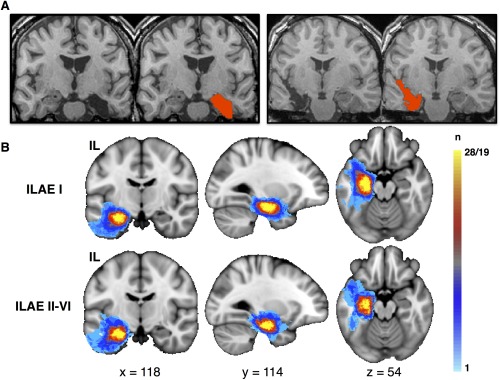
Resection and postoperative outcome. (A) Postoperative T1‐weighted magnetic resonance imaging of a left amygdalohippocampectomy via subtemporal access (left) and a right amygdalohippocampectomy via transsylvian access (right). The red area indicates the manually delineated surgical lacuna from which volumes were determined and resection mapping was performed. (B) Resection load in standard space according to postoperative outcome. Voxels are color‐coded according to the number of times a given voxel was included in the surgical lacuna (light blue, voxel was included in resection in 1 patient; yellow, voxel was included in resection in all patients within each group). There are no obvious visual differences between lesion extent and outcome, which was confirmed by statistical analysis of individual resection volumes (see main text). IL = ipsilateral; ILAE = International League Against Epilepsy; n = number of patients. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.annalsofneurology.org.]
