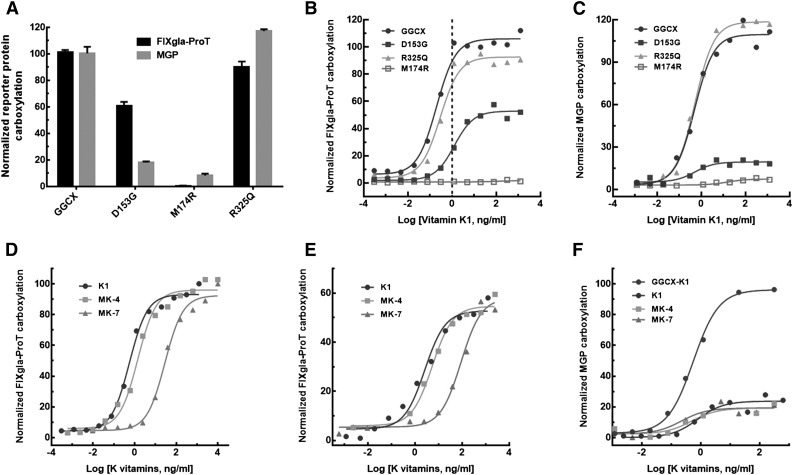
Figure 5.
Characterization of the 3 identified GGCX mutations using the established cell-based assay. (A) Carboxylation of FIXgla-ProT (black bars) and MGP (gray bars) by wild-type GGCX, GGCXD153G, GGCXM174R, and GGCXR325Q in GGCX-deficient cells in the presence of 5 µg/mL vitamin K1. (B) Carboxylation of FIXgla-ProT by wild-type GGCX (circles), GGCXD153G (solid squares), GGCXM174R (open squares), and GGCXR325Q (triangles) with increasing concentrations of vitamin K1; the vertical dashed line indicates the presumed physiological concentration of vitamin K1. (C) Carboxylation of MGP by the wild-type GGCX, GGCXD153G, GGCXM174R, and GGCXR325Q with increasing concentrations of vitamin K1 as in panel B. (D) Carboxylation of FIXgla-ProT by wild-type GGCX with increasing concentrations of vitamin K1 (circles), MK-4 (squares), and MK-7 (triangles). (E) Carboxylation of FIXgla-ProT by GGCXD153G with increasing concentrations of K vitamins as in panel D. (F) Carboxylation of MGP by GGCXD153G with increasing concentrations of K vitamins as in panel D. Carboxylation of MGP by the wild-type GGCX with vitamin K1 was used as a control (darker circles).