Figure 4.
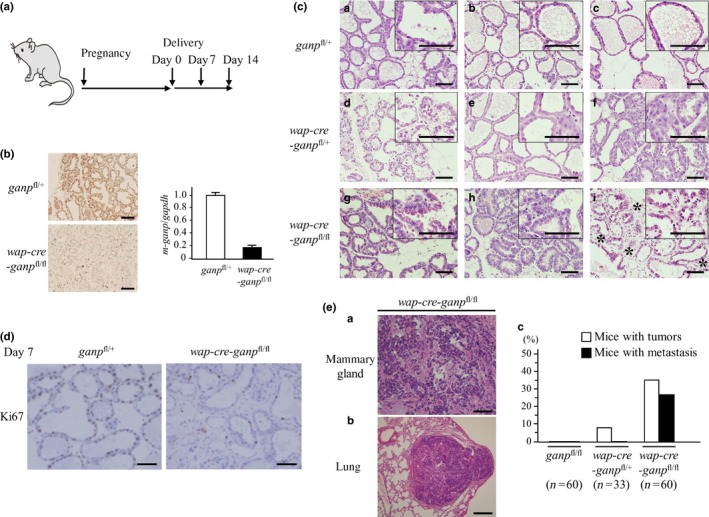
Impaired differentiation of mammary gland cells in ganp‐deficient mice. (A) Conditional targeting of the ganp gene in mammary gland cells from wap‐cre transgenic mice. (B) GANP expression was markedly decreased in wap‐cre‐ganp fl/fl mice compared with control mice after pregnancy on day 14. Scale bar = 100 μm (left). Real‐time PCR showed an 80% reduction in ganp transcripts in mammary glands from wap‐cre‐ganp fl/fl mice compared with control mice (right). Each column represents results from a single mouse analyzed in triplicate with error bars as SD. Results are normalized to the ganp fl/+ mouse. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) After pregnancy, the mice showed impaired differentiation of mammary gland cells with minimal lactic acid production, and abnormal gland architecture was observed on days 0 (a–c), 7 (d–f), and 14 (g–i) after delivery. Asterisks indicate fibrotic changes in the interglandular areas of mammary glands. Images at higher magnification are shown in the insets. Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Comparison of Ki67 positivity in mammary epithelial cells from control and wap‐cre‐ganp fl/fl mice. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) wap‐cre‐ganp fl/fl mice developed mammary gland tumors with lung metastasis after aging (a,b). Scale bar = 100 μm (a) and 200 μm (b). Incidence of mammary gland tumors in primiparous female mice. Mice with tumors are represented by white columns; those with lung metastasis are represented by black columns (c).
