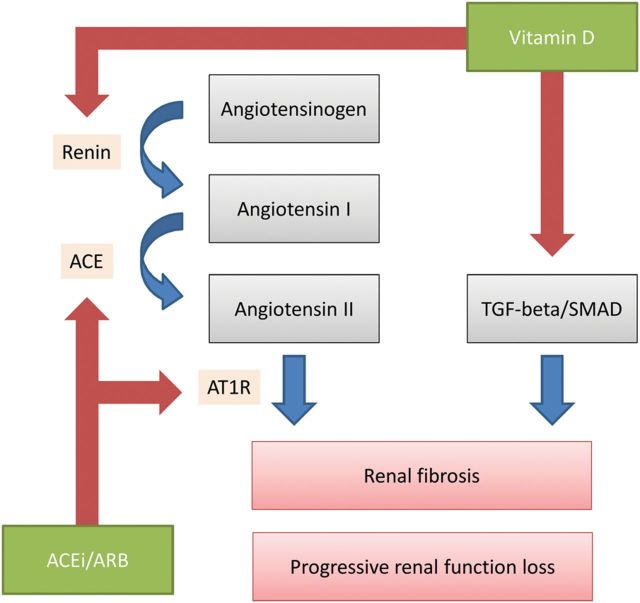
FIGURE 1:
Schematic representation of complementary renoprotective actions of ACEi/ARB and vitamin D in chronic kidney disease. Vitamin D may provide renoprotection through RAAS-mediated effects, i.e. by suppression of renin gene expression. This effect is through VDR signaling. The second renoprotective pathway of vitamin D is through reduction of TGF-beta/SMAD signaling. Negative regulation indicated by blue arrows, positive regulation by red arrows. ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; AT1R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; TGF-beta, transforming growth factor-beta. See text for references.